This is the multi-page printable view of this section.
Click here to print.
Return to the regular view of this page.
Curated Package management
Managing EKS Anywhere Curated Packages
EKS Anywhere Curated Packages make it easy to install, configure, and maintain operational components in EKS Anywhere clusters. EKS Anywhere Curated Packages are built, tested, and distributed by AWS to use with EKS Anywhere clusters as part of EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscriptions.
See Prerequisites
to get started.
Check out EKS Anywhere curated packages concepts
for more details.
1 - Overview of curated packages
Components of EKS Anywhere curated packages consist of a controller, a CLI, and artifacts.
Package controller
The package controller is responsible for installing, upgrading, configuring, and removing packages from the cluster. It performs these actions by watching the package and packagebundle custom resources. Moreover, it uses the packagebundle to determine which packages to run and sets appropriate configuration values.
Packages custom resources map to helm charts that the package controller uses to install packages workloads (such as cluster-autoscaler or metrics-server) on your clusters. The packagebundle object is the mapping between the package name and the specific helm chart and images that will be installed.
The package controller only runs on the management cluster, including single-node clusters, to perform the above outlined responsibilities. However, packages may be installed on both management and workload clusters. For more information, see the guide on installing packages on workload clusters.
Package release information is stored in a package bundle manifest. The package controller will continually monitor and download new package bundles. When a new package bundle is downloaded, it will show up as “available” in the PackageBundleController resource’s status.detail field. A package bundle upgrade always requires manual intervention as outlined in the package bundles
docs.
Any changes to a package custom resource will trigger an install, upgrade, configuration or removal of that package. The package controller will use ECR or private registry to get all resources including bundle, helm charts, and container images.
You may install the package controller
after cluster creation to take advantage of curated package features.
Packages CLI
The Curated Packages CLI provides the user experience required to manage curated packages.
Through the CLI, a user is able to discover, create, delete, and upgrade curated packages to a cluster.
These functionalities can be achieved during and after an EKS Anywhere cluster is created.
The CLI provides both imperative and declarative mechanisms to manage curated packages. These
packages will be included as part of a packagebundle that will be provided by the EKS Anywhere team.
Whenever a user requests a package creation through the CLI (eksctl anywhere create package), a custom resource is created on the cluster
indicating the existence of a new package that needs to be installed. When a user executes a delete operation (eksctl anywhere delete package),
the custom resource will be removed from the cluster indicating the need for uninstalling a package.
An upgrade through the CLI (eksctl anywhere upgrade packages) upgrades all packages to the latest release.
Please check out Install EKS Anywhere
to install the eksctl anywhere CLI on your machine.
The create cluster page for each EKS Anywhere provider
describes how to configure and install curated packages at cluster creation time.
Curated packages artifacts
There are three types of build artifacts for packages: the container images, the helm charts and the package bundle manifests. The container images, helm charts and bundle manifests for all of the packages will be built and stored in EKS Anywhere ECR repository. Each package may have multiple versions specified in the packages bundle. The bundle will reference the helm chart tag in the ECR repository. The helm chart will reference the container images for the package.
Installing packages on workload clusters

The package controller only runs on the management cluster. It determines which cluster to install your package on based on the namespace specified in the Package resource.
See an example package below:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-hello-eks-anywhere
namespace: eksa-packages-wk0
spec:
config: |
title: "My Hello"
packageName: hello-eks-anywhere
targetNamespace: default
By specifying metadata.namespace: eksa-packages-wk0, the package controller will install the resource on workload cluster wk0.
The pattern for these namespaces is always eksa-packages-<cluster-name>.
By specifying spec.targetNamespace: default, the package controller will install the hello-eks-anywhere package helm chart in the default namespace in cluster wk0.
2 - Prerequisites
Prerequisites for using curated packages
Prerequisites
Before installing any curated packages for EKS Anywhere, do the following:
-
Check that the cluster Kubernetes version is v1.21 or above. For example, you could run kubectl get cluster -o yaml <cluster-name> | grep -i kubernetesVersion
-
Check that the version of eksctl anywhere is v0.11.0 or above with the eksctl anywhere version command.
-
It is recommended that the package controller is only installed on the management cluster.
-
Check the existence of package controller:
kubectl get pods -n eksa-packages | grep "eks-anywhere-packages"
If the returned result is empty, you need to install the package controller.
-
Install the package controller if it is not installed:
Install the package controller
Note This command is temporarily provided to ease integration with curated packages. This command will be deprecated in the future
eksctl anywhere install packagecontroller -f $CLUSTER_NAME.yaml
To request a free trial, talk to your Amazon representative or connect with one here
.
Identify AWS account ID for ECR packages registry
The AWS account ID for ECR packages registry depends on the EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscription.
- For EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscriptions purchased through the AWS console or APIs the AWS account ID for ECR packages registry varies depending on the region the Enterprise Subscription was purchased. Reference the table in the expanded output below for a mapping of AWS Regions to ECR package registries.
Expand for packages registry to AWS Region table
| AWS Region |
Packages Registry Account |
| us-west-2 |
346438352937 |
| us-west-1 |
440460740297 |
| us-east-1 |
331113665574 |
| us-east-2 |
297090588151 |
| ap-east-1 |
804323328300 |
| ap-northeast-1 |
143143237519 |
| ap-northeast-2 |
447311122189 |
| ap-south-1 |
357015164304 |
| ap-south-2 |
388483641499 |
| ap-southeast-1 |
654894141437 |
| ap-southeast-2 |
299286866837 |
| ap-southeast-3 |
703305448174 |
| ap-southeast-4 |
106475008004 |
| af-south-1 |
783635962247 |
| ca-central-1 |
064352486547 |
| eu-central-1 |
364992945014 |
| eu-central-2 |
551422459769 |
| eu-north-1 |
826441621985 |
| eu-south-1 |
787863792200 |
| eu-west-1 |
090204409458 |
| eu-west-2 |
371148654473 |
| eu-west-3 |
282646289008 |
| il-central-1 |
131750224677 |
| me-central-1 |
454241080883 |
| me-south-1 |
158698011868 |
| sa-east-1 |
517745584577 |
- For EKS Anywhere Curated Packages trials or EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscriptions purchased before October 2023 the AWS account ID for ECR packages registry is
783794618700. This supports pulling images from the following regions.
Expand for AWS Regions table
| AWS Region |
| us-east-2 |
| us-east-1 |
| us-west-1 |
| us-west-2 |
| ap-northeast-3 |
| ap-northeast-2 |
| ap-southeast-1 |
| ap-southeast-2 |
| ap-northeast-1 |
| ca-central-1 |
| eu-central-1 |
| eu-west-1 |
| eu-west-2 |
| eu-west-3 |
| eu-north-1 |
| sa-east-1 |
After identifying the AWS account ID; export it for further reference. Example
export ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT=346438352937
Setup authentication to use curated packages
When you have been notified that your account has been given access to curated packages, create an IAM user in your account with a policy that only allows ECR read access to the Curated Packages repository; similar to this:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "ECRRead",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:DescribeImageScanFindings",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:DescribeRegistry",
"ecr:DescribePullThroughCacheRules",
"ecr:DescribeImageReplicationStatus",
"ecr:ListTagsForResource",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:DescribeImages",
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:*:<ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT>:repository/*"
},
{
"Sid": "ECRLogin",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Note Use the corresponding EKSA_AWS_REGION prior to cluster creation to choose which region to pull form.
Create credentials for this user and set and export the following environment variables:
export EKSA_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your*access*id"
export EKSA_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your*secret*key"
export EKSA_AWS_REGION="aws*region"
Make sure you are authenticated with the AWS CLI
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your*access*id"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your*secret*key"
aws sts get-caller-identity
Login to docker
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-west-2 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT.dkr.ecr.$EKSA_AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
Verify you can pull an image
docker pull $ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT.dkr.ecr.$EKSA_AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/emissary-ingress/emissary:v3.9.1-828e7d186ded23e54f6bd95a5ce1319150f7e325
If the image downloads successfully, it worked!
Prepare for using curated packages for airgapped environments
If you are running in an airgapped environment and you set up a local registry mirror, you can copy curated packages from Amazon ECR to your local registry mirror with the following command.
The $BUNDLE_RELEASE_YAML_PATH should be set to the eks-anywhere-downloads/bundle-release.yaml location where you unpacked the tarball from theeksctl anywhere download artifacts command. The $REGISTRY_MIRROR_CERT_PATH and $REGISTRY_MIRROR_URL values must be the same as the registryMirrorConfiguration in your EKS Anywhere cluster specification.
eksctl anywhere copy packages \
--bundle ${BUNDLE_RELEASE_YAML_PATH} \
--dst-cert ${REGISTRY_MIRROR_CERT_PATH} \
${REGISTRY_MIRROR_URL}
Once the curated packages images are in your local registry mirror, you must configure the curated packages controller to use your local registry mirror post-cluster creation. Configure the defaultImageRegistry and defaultRegistry settings for the PackageBundleController to point to your local registry mirror by applying a similar yaml definition as the one below to your standalone or management cluster. Existing PackageBundleController can be changed, and you do not need to deploy a new PackageBundleController. See the Packages configuration documentation
for more information.
apiVersion: anywhere.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: PackageBundleController
metadata:
name: eksa-packages-bundle-controller
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
defaultImageRegistry: ${REGISTRY_MIRROR_URL}/curated-packages
defaultRegistry: ${REGISTRY_MIRROR_URL}/eks-anywhere
Discover curated packages
You can get a list of the available packages from the command line:
export CLUSTER_NAME=<your-cluster-name>
export KUBECONFIG=${PWD}/${CLUSTER_NAME}/${CLUSTER_NAME}-eks-a-cluster.kubeconfig
eksctl anywhere list packages --kube-version 1.27
Example command output:
Package Version(s)
------- ----------
hello-eks-anywhere 0.1.2-a6847010915747a9fc8a412b233a2b1ee608ae76
adot 0.25.0-c26690f90d38811dbb0e3dad5aea77d1efa52c7b
cert-manager 1.9.1-dc0c845b5f71bea6869efccd3ca3f2dd11b5c95f
cluster-autoscaler 9.21.0-1.23-5516c0368ff74d14c328d61fe374da9787ecf437
harbor 2.5.1-ee7e5a6898b6c35668a1c5789aa0d654fad6c913
metallb 0.13.7-758df43f8c5a3c2ac693365d06e7b0feba87efd5
metallb-crds 0.13.7-758df43f8c5a3c2ac693365d06e7b0feba87efd5
metrics-server 0.6.1-eks-1-23-6-c94ed410f56421659f554f13b4af7a877da72bc1
emissary 3.3.0-cbf71de34d8bb5a72083f497d599da63e8b3837b
emissary-crds 3.3.0-cbf71de34d8bb5a72083f497d599da63e8b3837b
prometheus 2.41.0-b53c8be243a6cc3ac2553de24ab9f726d9b851ca
Generate curated packages configuration
The example shows how to install the harbor package from the curated package list
.
export CLUSTER_NAME=<your-cluster-name>
eksctl anywhere generate package harbor --cluster ${CLUSTER_NAME} --kube-version 1.27 > harbor-spec.yaml
3 - Packages configuration
Full EKS Anywhere configuration reference for curated packages
This is a generic template with detailed descriptions below for reference. To generate your own package configuration, follow instructions from Package Management
section and modify it using descriptions below.
apiVersion: anywhere.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: PackageBundleController
metadata:
name: eksa-packages-bundle-controller
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
activeBundle: v1-21-83
defaultImageRegistry: 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
defaultRegistry: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
privateRegistry: ""
upgradeCheckInterval: 24h0m0s
---
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: PackageBundle
metadata:
name: package-bundle
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packages:
- name: hello-eks-anywhere
source:
repository: hello-eks-anywhere
versions:
- digest: sha256:c31242a2f94a58017409df163debc01430de65ded6bdfc5496c29d6a6cbc0d94
images:
- digest: sha256:26e3f2f9aa546fee833218ece3fe7561971fd905cef40f685fd1b5b09c6fb71d
repository: hello-eks-anywhere
name: 0.1.1-083e68edbbc62ca0228a5669e89e4d3da99ff73b
schema: H4sIAJc5EW...
---
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-hello-eks-anywhere
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
config: |
title: "My Hello"
packageName: hello-eks-anywhere
targetNamespace: eksa-packages
API Reference
Packages:
packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
Resource Types:
PackageBundleController
↩ Parent
PackageBundleController is the Schema for the packagebundlecontroller API.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| apiVersion |
string |
packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1 |
true |
| kind |
string |
PackageBundleController |
true |
| metadata |
object |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the `metadata` field. |
true |
| spec |
object |
PackageBundleControllerSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundleController.
|
false |
| status |
object |
PackageBundleControllerStatus defines the observed state of PackageBundleController.
|
false |
PackageBundleController.spec
↩ Parent
PackageBundleControllerSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundleController.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| activeBundle |
string |
ActiveBundle is name of the bundle from which packages should be sourced.
|
false |
| bundleRepository |
string |
Repository portion of an OCI address to the bundle
Default: eks-anywhere-packages-bundles
|
false |
| createNamespace |
boolean |
Allow target namespace creation by the controller
Default: false
|
false |
| defaultImageRegistry |
string |
DefaultImageRegistry for pulling images
Default: 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
|
false |
| defaultRegistry |
string |
DefaultRegistry for pulling helm charts and the bundle
Default: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
|
false |
| logLevel |
integer |
LogLevel controls the verbosity of logging in the controller.
Format: int32
|
false |
| privateRegistry |
string |
PrivateRegistry is the registry being used for all images, charts and bundles
|
false |
| upgradeCheckInterval |
string |
UpgradeCheckInterval is the time between upgrade checks.
The format is that of time's ParseDuration.
Default: 24h
|
false |
| upgradeCheckShortInterval |
string |
UpgradeCheckShortInterval time between upgrade checks if there is a problem.
The format is that of time's ParseDuration.
Default: 1h
|
false |
PackageBundleController.status
↩ Parent
PackageBundleControllerStatus defines the observed state of PackageBundleController.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| detail |
string |
Detail of the state.
|
false |
| spec |
object |
Spec previous settings
|
false |
| state |
enum |
State of the bundle controller.
Enum: ignored, active, disconnected, upgrade available
|
false |
PackageBundleController.status.spec
↩ Parent
Spec previous settings
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| activeBundle |
string |
ActiveBundle is name of the bundle from which packages should be sourced.
|
false |
| bundleRepository |
string |
Repository portion of an OCI address to the bundle
Default: eks-anywhere-packages-bundles
|
false |
| createNamespace |
boolean |
Allow target namespace creation by the controller
Default: false
|
false |
| defaultImageRegistry |
string |
DefaultImageRegistry for pulling images
Default: 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
|
false |
| defaultRegistry |
string |
DefaultRegistry for pulling helm charts and the bundle
Default: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
|
false |
| logLevel |
integer |
LogLevel controls the verbosity of logging in the controller.
Format: int32
|
false |
| privateRegistry |
string |
PrivateRegistry is the registry being used for all images, charts and bundles
|
false |
| upgradeCheckInterval |
string |
UpgradeCheckInterval is the time between upgrade checks.
The format is that of time's ParseDuration.
Default: 24h
|
false |
| upgradeCheckShortInterval |
string |
UpgradeCheckShortInterval time between upgrade checks if there is a problem.
The format is that of time's ParseDuration.
Default: 1h
|
false |
PackageBundle
↩ Parent
PackageBundle is the Schema for the packagebundle API.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| apiVersion |
string |
packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1 |
true |
| kind |
string |
PackageBundle |
true |
| metadata |
object |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the `metadata` field. |
true |
| spec |
object |
PackageBundleSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundle.
|
false |
| status |
object |
PackageBundleStatus defines the observed state of PackageBundle.
|
false |
PackageBundle.spec
↩ Parent
PackageBundleSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundle.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| packages |
[]object |
Packages supported by this bundle.
|
true |
| minControllerVersion |
string |
Minimum required packages controller version
|
false |
PackageBundle.spec.packages[index]
↩ Parent
BundlePackage specifies a package within a bundle.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| source |
object |
Source location for the package (probably a helm chart).
|
true |
| name |
string |
Name of the package.
|
false |
| workloadonly |
boolean |
WorkloadOnly specifies if the package should be installed only on the workload cluster
|
false |
PackageBundle.spec.packages[index].source
↩ Parent
Source location for the package (probably a helm chart).
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| repository |
string |
Repository within the Registry where the package is found.
|
true |
| versions |
[]object |
Versions of the package supported by this bundle.
|
true |
| registry |
string |
Registry in which the package is found.
|
false |
PackageBundle.spec.packages[index].source.versions[index]
↩ Parent
SourceVersion describes a version of a package within a repository.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| digest |
string |
Digest is a checksum value identifying the version of the package and its contents.
|
true |
| name |
string |
Name is a human-friendly description of the version, e.g. "v1.0".
|
true |
| dependencies |
[]string |
Dependencies to be installed before the package
|
false |
| images |
[]object |
Images is a list of images used by this version of the package.
|
false |
| schema |
string |
Schema is a base64 encoded, gzipped json schema used to validate package configurations.
|
false |
PackageBundle.spec.packages[index].source.versions[index].images[index]
↩ Parent
VersionImages is an image used by a version of a package.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| digest |
string |
Digest is a checksum value identifying the version of the package and its contents.
|
true |
| repository |
string |
Repository within the Registry where the package is found.
|
true |
PackageBundle.status
↩ Parent
PackageBundleStatus defines the observed state of PackageBundle.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| state |
enum |
PackageBundleStateEnum defines the observed state of PackageBundle.
Enum: available, ignored, invalid, controller upgrade required
|
true |
| spec |
object |
PackageBundleSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundle.
|
false |
PackageBundle.status.spec
↩ Parent
PackageBundleSpec defines the desired state of PackageBundle.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| packages |
[]object |
Packages supported by this bundle.
|
true |
| minControllerVersion |
string |
Minimum required packages controller version
|
false |
PackageBundle.status.spec.packages[index]
↩ Parent
BundlePackage specifies a package within a bundle.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| source |
object |
Source location for the package (probably a helm chart).
|
true |
| name |
string |
Name of the package.
|
false |
| workloadonly |
boolean |
WorkloadOnly specifies if the package should be installed only on the workload cluster
|
false |
PackageBundle.status.spec.packages[index].source
↩ Parent
Source location for the package (probably a helm chart).
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| repository |
string |
Repository within the Registry where the package is found.
|
true |
| versions |
[]object |
Versions of the package supported by this bundle.
|
true |
| registry |
string |
Registry in which the package is found.
|
false |
PackageBundle.status.spec.packages[index].source.versions[index]
↩ Parent
SourceVersion describes a version of a package within a repository.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| digest |
string |
Digest is a checksum value identifying the version of the package and its contents.
|
true |
| name |
string |
Name is a human-friendly description of the version, e.g. "v1.0".
|
true |
| dependencies |
[]string |
Dependencies to be installed before the package
|
false |
| images |
[]object |
Images is a list of images used by this version of the package.
|
false |
| schema |
string |
Schema is a base64 encoded, gzipped json schema used to validate package configurations.
|
false |
PackageBundle.status.spec.packages[index].source.versions[index].images[index]
↩ Parent
VersionImages is an image used by a version of a package.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| digest |
string |
Digest is a checksum value identifying the version of the package and its contents.
|
true |
| repository |
string |
Repository within the Registry where the package is found.
|
true |
Package
↩ Parent
Package is the Schema for the package API.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| apiVersion |
string |
packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1 |
true |
| kind |
string |
Package |
true |
| metadata |
object |
Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation for the fields of the `metadata` field. |
true |
| spec |
object |
PackageSpec defines the desired state of an package.
|
false |
| status |
object |
PackageStatus defines the observed state of Package.
|
false |
Package.spec
↩ Parent
PackageSpec defines the desired state of an package.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| packageName |
string |
PackageName is the name of the package as specified in the bundle.
|
true |
| config |
string |
Config for the package.
|
false |
| packageVersion |
string |
PackageVersion is a human-friendly version name or sha256 checksum for the package, as specified in the bundle.
|
false |
| targetNamespace |
string |
TargetNamespace defines where package resources will be deployed.
|
false |
Package.status
↩ Parent
PackageStatus defines the observed state of Package.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| currentVersion |
string |
Version currently installed.
|
true |
| source |
object |
Source associated with the installation.
|
true |
| detail |
string |
Detail of the state.
|
false |
| spec |
object |
Spec previous settings
|
false |
| state |
enum |
State of the installation.
Enum: initializing, installing, installing dependencies, installed, updating, uninstalling, unknown
|
false |
| targetVersion |
string |
Version to be installed.
|
false |
| upgradesAvailable |
[]object |
UpgradesAvailable indicates upgraded versions in the bundle.
|
false |
Package.status.source
↩ Parent
Source associated with the installation.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| digest |
string |
Digest is a checksum value identifying the version of the package and its contents.
|
true |
| registry |
string |
Registry in which the package is found.
|
true |
| repository |
string |
Repository within the Registry where the package is found.
|
true |
| version |
string |
Versions of the package supported.
|
true |
Package.status.spec
↩ Parent
Spec previous settings
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| packageName |
string |
PackageName is the name of the package as specified in the bundle.
|
true |
| config |
string |
Config for the package.
|
false |
| packageVersion |
string |
PackageVersion is a human-friendly version name or sha256 checksum for the package, as specified in the bundle.
|
false |
| targetNamespace |
string |
TargetNamespace defines where package resources will be deployed.
|
false |
Package.status.upgradesAvailable[index]
↩ Parent
PackageAvailableUpgrade details the package’s available upgrade versions.
| Name |
Type |
Description |
Required |
| tag |
string |
Tag is a specific version number or sha256 checksum for the package upgrade.
|
true |
| version |
string |
Version is a human-friendly version name for the package upgrade.
|
true |
4 - Managing the package controller
Installing the package controller
Important
The package controller installation creates a package bundle controller resource for each cluster, thus allowing each to activate a different package bundle version. Ideally, you should never delete this resource because it would mean losing that information and upon re-installing, the latest bundle would be selected. However, you can always go back to the previous bundle version. For more information, see
Managing package bundles.
The package controller is typically installed during cluster creation, but may be disabled intentionally in your cluster.yaml by setting spec.packages.disable to true.
If you created a cluster without the package controller or if the package controller was not properly configured, you may need to manually install it.
-
Enable the package controller in your cluster.yaml, if it was previously disabled:
apiVersion: anywhere.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: mgmt
spec:
packages:
disable: false
-
Make sure you are authenticated with the AWS CLI. Use the credentials you set up for packages. These credentials should have limited capabilities
:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your*access*id"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your*secret*key"
export EKSA_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your*access*id"
export EKSA_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your*secret*key"
-
Verify your credentials are working:
aws sts get-caller-identity
-
Authenticate docker to the private AWS ECR registry with your AWS credentials. Reference prerequisites to identity the AWS account that houses the EKS Anywhere packages artifacts. Authentication is required to pull images from it.
aws ecr get-login-password | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT.dkr.ecr.$EKSA_AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
-
Verify you can pull an image from the packages registry:
docker pull $ECR_PACKAGES_ACCOUNT.dkr.ecr.$EKSA_AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com/emissary-ingress/emissary:v3.9.1-828e7d186ded23e54f6bd95a5ce1319150f7e325
If the image downloads successfully, it worked!
-
Now, install the package controller using the EKS Anywhere Packages CLI:
eksctl anywhere install packagecontroller -f cluster.yaml
The package controller should now be installed!
-
Use kubectl to check the eks-anywhere-packages pod is running in your management cluster:
kubectl get pods -n eksa-packages
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
eks-anywhere-packages-55bc54467c-jfhgp 1/1 Running 0 21s
Updating the package credentials
You may need to create or update your credentials which you can do with a command like this. Set the environment variables to the proper values before running the command.
kubectl delete secret -n eksa-packages aws-secret
kubectl create secret -n eksa-packages generic aws-secret \
--from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=${EKSA_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID} \
--from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=${EKSA_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} \
--from-literal=REGION=${EKSA_AWS_REGION}
Upgrade the packages controller
EKS Anywhere v0.15.0 (packages controller v0.3.9+) and onwards includes support for the eks-anywhere-packages controller as a self-managed package feature. The package controller now upgrades automatically according to the version specified within the management cluster’s selected package bundle.
For any version prior to v0.3.X, manual steps must be executed to upgrade.
Important
This operation may change your cluster’s selected package bundle to the latest version. However, you can always go back to the previous bundle version. For more information, see
Managing package bundles.
To manually upgrade the package controller, do the following:
- Ensure the namespace will be kept
kubectl annotate namespaces eksa-packages helm.sh/resource-policy=keep
- Uninstall the eks-anywhere-packages helm release
helm uninstall -n eksa-packages eks-anywhere-packages
- Remove the secret called aws-secret (we will need credentials when installing the new version)
kubectl delete secret -n eksa-packages aws-secret
- Install the new version using the latest eksctl-anywhere binary on your management cluster
eksctl anywhere install packagecontroller -f eksa-mgmt-cluster.yaml
5 - Packages regional ECR migration
Migrating EKS Anywhere Curated Packages to latest regional ECR repositories
When you purchase an EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscription through the Amazon EKS console or APIs, the AWS account that purchased the subscription is automatically granted access to EKS Anywhere Curated Packages in the AWS Region where the subscription is created. If you received trial access to EKS Anywhere Curated Packages or if you have an EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscription that was created before October 2023, then you need to migrate your EKS Anywhere Curated Packages configuration to use the latest ECR regional repositories. This process would cause all the Curated Packages installed on the cluster to rollout and be deployed from the latest ECR regional repositories.
Expand for packages registry to AWS Region table
| AWS Region |
Packages Registry Account |
| us-west-2 |
346438352937 |
| us-west-1 |
440460740297 |
| us-east-1 |
331113665574 |
| us-east-2 |
297090588151 |
| ap-east-1 |
804323328300 |
| ap-northeast-1 |
143143237519 |
| ap-northeast-2 |
447311122189 |
| ap-south-1 |
357015164304 |
| ap-south-2 |
388483641499 |
| ap-southeast-1 |
654894141437 |
| ap-southeast-2 |
299286866837 |
| ap-southeast-3 |
703305448174 |
| ap-southeast-4 |
106475008004 |
| af-south-1 |
783635962247 |
| ca-central-1 |
064352486547 |
| eu-central-1 |
364992945014 |
| eu-central-2 |
551422459769 |
| eu-north-1 |
826441621985 |
| eu-south-1 |
787863792200 |
| eu-west-1 |
090204409458 |
| eu-west-2 |
371148654473 |
| eu-west-3 |
282646289008 |
| il-central-1 |
131750224677 |
| me-central-1 |
454241080883 |
| me-south-1 |
158698011868 |
| sa-east-1 |
517745584577 |
Steps for Migration
-
Ensure you have an active EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscription. For more information, refer Purchase subscriptions.
-
If the AWS account that created the EKS Anywhere Enterprise Subscription through the Amazon EKS console or APIs and the AWS IAM user credentials for curated packages on your existing cluster are different, you need to update the aws-secret object on the cluster with new credentials. Refer Updating the package credentials
.
-
Edit the ecr-credential-provider-package package on the cluster and update matchImages with the correct ECR package registry for the AWS Region where you created your subscription. Example, 346438352937.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com for us-west-2. Reference the table in the expanded output at the top of this page for a mapping of AWS Regions to ECR package registries.
kubectl edit package ecr-credential-provider-package -n eksa-packages-<cluster name>
This causes ecr-credential-provider-package pods to rollout and the kubelet is configured to use AWS credentials for pulling images from the new regional ECR packages registry.
-
Edit the PackageBundleController object on the cluster and set the defaultImageRegistry and defaultRegistry to point to the ECR package registry for the AWS Region where you created your subscription.
kubectl edit packagebundlecontroller <cluster name> -n eksa-packages
-
Restart the eks-anywhere-packages controller deployment.
kubectl rollout restart deployment eks-anywhere-packages -n eksa-packages
This step causes the package controller to pull down a new package bundle onto the cluster and marks the PackageBundleController as upgrade available. Example
NAMESPACE NAME ACTIVEBUNDLE STATE DETAIL
eksa-packages my-cluster-name v1-28-160 upgrade available v1-28-274 available
-
Edit the PackageBundleController object on the cluster and set the activeBundle field to the new bundle number that is available.
kubectl edit packagebundlecontroller <cluster name> -n eksa-packages
This step causes all the packages on the cluster to be reinstalled and pods rolled out from the new registry.
-
Edit the ecr-credential-provider-package package again and now set the sourceRegistry to point to the ECR package registry for the AWS Region where you created your subscription.
kubectl edit package ecr-credential-provider-package -n eksa-packages-<cluster name>
This causes ecr-credential-provider-package to be reinstalled from the new registry.
6 - Managing package bundles
Getting new package bundles
Package bundle resources are created and managed in the management cluster, so first set up the KUBECONFIG environment variable for the management cluster.
export KUBECONFIG=mgmt/mgmt-eks-a-cluster.kubeconfig
The EKS Anywhere package controller periodically checks upstream for the latest package bundle and applies it to your management cluster, except for when in an airgapped environment
. In that case, you would have to get the package bundle manually from outside of the airgapped environment and apply it to your management cluster.
To view the available packagebundles in your cluster, run the following:
kubectl get packagebundles -n eksa-packages
NAMESPACE NAME STATE
eksa-packages v1-27-125 available
To get a package bundle manually, you can use oras to pull the package bundle (bundle.yaml) from the public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere repository. (See the ORAS CLI official documentation
for more details)
oras pull public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere/eks-anywhere-packages-bundles:v1-27-latest
Downloading 1ba8253d19f9 bundle.yaml
Downloaded 1ba8253d19f9 bundle.yaml
Pulled [registry] public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere/eks-anywhere-packages-bundles:v1-27-latest
Use kubectl to apply the new package bundle to your cluster to make it available for use.
kubectl apply -f bundle.yaml
The package bundle should now be available for use in the management cluster.
kubectl get packagebundles -n eksa-packages
NAMESPACE NAME STATE
eksa-packages v1-27-125 available
eksa-packages v1-27-126 available
Activating a package bundle
There are multiple packagebundlecontrollers resources in the management cluster which allows for each cluster to activate different package bundle versions. The active package bundle determines the versions of the packages that are installed on that cluster.
To view which package bundle is active for each cluster, use the kubectl command to list the packagebundlecontrollers objects in the management cluster.
kubectl get packagebundlecontrollers -A
NAMESPACE NAME ACTIVEBUNDLE STATE DETAIL
eksa-packages mgmt v1-27-125 active
eksa-packages w01 v1-27-125 active
To upgrade the active package bundle for the target cluster, edit the packagebundlecontroller object on the cluster and set the activeBundle field to the new bundle number that is available.
kubectl edit packagebundlecontroller <cluster name> -n eksa-packages
7 - Configuration best practices
Best practices with curated packages
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
8 - Packages
List of EKS Anywhere curated packages
Curated package list
9 - Curated packages troubleshooting
Troubleshooting specific to curated packages
General debugging
The major component of Curated Packages is the package controller. If the container is not running or not running correctly, packages will not be installed. Generally it should be debugged like any other Kubernetes application. The first step is to check that the pod is running.
kubectl get pods -n eksa-packages
You should see at least two pods with running and one or more refresher completed.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
eks-anywhere-packages-69d7bb9dd9-9d47l 1/1 Running 0 14s
eksa-auth-refresher-w82nm 0/1 Completed 0 10s
The describe command might help to get more detail on why there is a problem:
kubectl describe pods -n eksa-packages
Logs of the controller can be seen in a normal Kubernetes fashion:
kubectl logs deploy/eks-anywhere-packages -n eksa-packages controller
To get the general state of the package controller, run the following command:
kubectl get packages,packagebundles,packagebundlecontrollers -A
You should see an active packagebundlecontroller and an available bundle. The packagebundlecontroller should indicate the active bundle. It may take a few minutes to download and activate the latest bundle. The state of the package in this example is installing and there is an error downloading the chart.
NAMESPACE NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
eksa-packages-sammy package.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/my-hello hello-eks-anywhere 42h installed 0.1.1-bc7dc6bb874632972cd92a2bca429a846f7aa785 0.1.1-bc7dc6bb874632972cd92a2bca429a846f7aa785 (latest)
eksa-packages-tlhowe package.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/my-hello hello-eks-anywhere 44h installed 0.1.1-083e68edbbc62ca0228a5669e89e4d3da99ff73b 0.1.1-083e68edbbc62ca0228a5669e89e4d3da99ff73b (latest)
NAMESPACE NAME STATE
eksa-packages packagebundle.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1-21-83 available
eksa-packages packagebundle.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1-23-70 available
eksa-packages packagebundle.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1-23-81 available
eksa-packages packagebundle.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1-23-82 available
eksa-packages packagebundle.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1-23-83 available
NAMESPACE NAME ACTIVEBUNDLE STATE DETAIL
eksa-packages packagebundlecontroller.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/sammy v1-23-70 upgrade available v1-23-83 available
eksa-packages packagebundlecontroller.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/tlhowe v1-21-83 active active
Package controller not running
If you do not see a pod or various resources for the package controller, it may be that it is not installed.
No resources found in eksa-packages namespace.
Most likely the cluster was created with an older version of the EKS Anywhere CLI. Curated packages became generally available with v0.11.0. Use the eksctl anywhere version command to verify you are running a new enough release and you can use the eksctl anywhere install packagecontroller command to install the package controller on an older release.
Error: this command is currently not supported
Error: this command is currently not supported
Curated packages became generally available with version v0.11.0. Use the version command to make sure you are running version v0.11.0 or later:
Error: cert-manager is not present in the cluster
Error: curated packages cannot be installed as cert-manager is not present in the cluster
This is most likely caused by an action to install curated packages at a workload cluster with eksctl anywhere version older than v0.12.0. In order to use packages on workload clusters, please upgrade eksctl anywhere version to v0.12+. The package manager will remotely manage packages on the workload cluster from the management cluster.
Package registry authentication
Error: ImagePullBackOff on Package
If a package fails to start with ImagePullBackOff:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
generated-harbor-jobservice-564d6fdc87 0/1 ImagePullBackOff 0 2d23h
If a package pod cannot pull images, you may not have your AWS credentials set up properly. Verify that your credentials are working properly.
Make sure you are authenticated with the AWS CLI. Use the credentials you set up for packages. These credentials should have limited capabilities
:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="your*access*id"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="your*secret*key"
aws sts get-caller-identity
Login to docker
aws ecr get-login-password |docker login --username AWS --password-stdin 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
Verify you can pull an image
docker pull 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/emissary-ingress/emissary:v3.5.1-bf70150bcdfe3a5383ec8ad9cd7eea801a0cb074
If the image downloads successfully, it worked!
You may need to create or update your credentials which you can do with a command like this. Set the environment variables to the proper values before running the command.
kubectl delete secret -n eksa-packages aws-secret
kubectl create secret -n eksa-packages generic aws-secret --from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=${EKSA_AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID} --from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=${EKSA_AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY} --from-literal=REGION=${EKSA_AWS_REGION}
Package on workload clusters
Starting at eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster. While interacting with the package resources by the following commands for a workload cluster, please make sure the kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster.
Package manager is not managing packages on workload cluster
If the package manager is not managing packages on a workload cluster, make sure the management cluster has various resources for the workload cluster:
kubectl get packages,packagebundles,packagebundlecontrollers -A
You should see a PackageBundleController for the workload cluster named with the name of the workload cluster and the status should be set. There should be a namespace for the workload cluster as well:
kubectl get ns | grep eksa-packages
Create a PackageBundlecController for the workload cluster if it does not exist (where billy here is the cluster name):
cat <<! | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: PackageBundleController
metadata:
name: billy
namespace: eksa-packages
!
Workload cluster is disconnected
Cluster is disconnected:
NAMESPACE NAME ACTIVEBUNDLE STATE DETAIL
eksa-packages packagebundlecontroller.packages.eks.amazonaws.com/billy disconnected initializing target client: getting kubeconfig for cluster "billy": Secret "billy-kubeconfig" not found
In the example above, the secret does not exist which may be that the management cluster is not managing the cluster, the PackageBundleController name is wrong or the secret was deleted.
This also may happen if the management cluster cannot communicate with the workload cluster or the workload cluster was deleted, although the detail would be different.
Error: the server doesn’t have a resource type “packages”
All packages are remotely managed by the management cluster, and packages, packagebundles, and packagebundlecontrollers resources are all deployed on the management cluster. Please make sure the kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster while interacting with package-related resources.
A package command run on a cluster that does not seem to be managed by the management cluster. To get a list of the clusters managed by the management cluster run the following command:
eksctl anywhere get packagebundlecontroller
NAME ACTIVEBUNDLE STATE DETAIL
billy v1-21-87 active
There will be one packagebundlecontroller for each cluster that is being managed. The only valid cluster name in the above example is billy.
10 - ADOT Configuration
OpenTelemetry Collector provides a vendor-agnostic solution to receive, process and export telemetry data. It removes the need to run, operate, and maintain multiple agents/collectors. ADOT Collector is an AWS-supported distribution of the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for ADOT
10.1 - ADOT with AMP and AMG
This tutorial demonstrates how to config the ADOT package to scrape metrics from an EKS Anywhere cluster, and send them to Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus
(AMP) and Amazon Managed Grafana
(AMG).
This tutorial walks through the following procedures:
Note
- We included
Test sections below for critical steps to help users to validate they have completed such procedure properly. We recommend going through them in sequence as checkpoints of the progress.
- We recommend creating all resources in the
us-west-2 region.
Create an AMP workspace
An AMP workspace is created to receive metrics from the ADOT package, and respond to query requests from AMG. Follow steps below to complete the set up:
-
Open the AMP console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/prometheus/.
-
Choose region us-west-2 from the top right corner.
-
Click on Create to create a workspace.
-
Type a workspace alias (adot-amp-test as an example), and click on Create workspace.
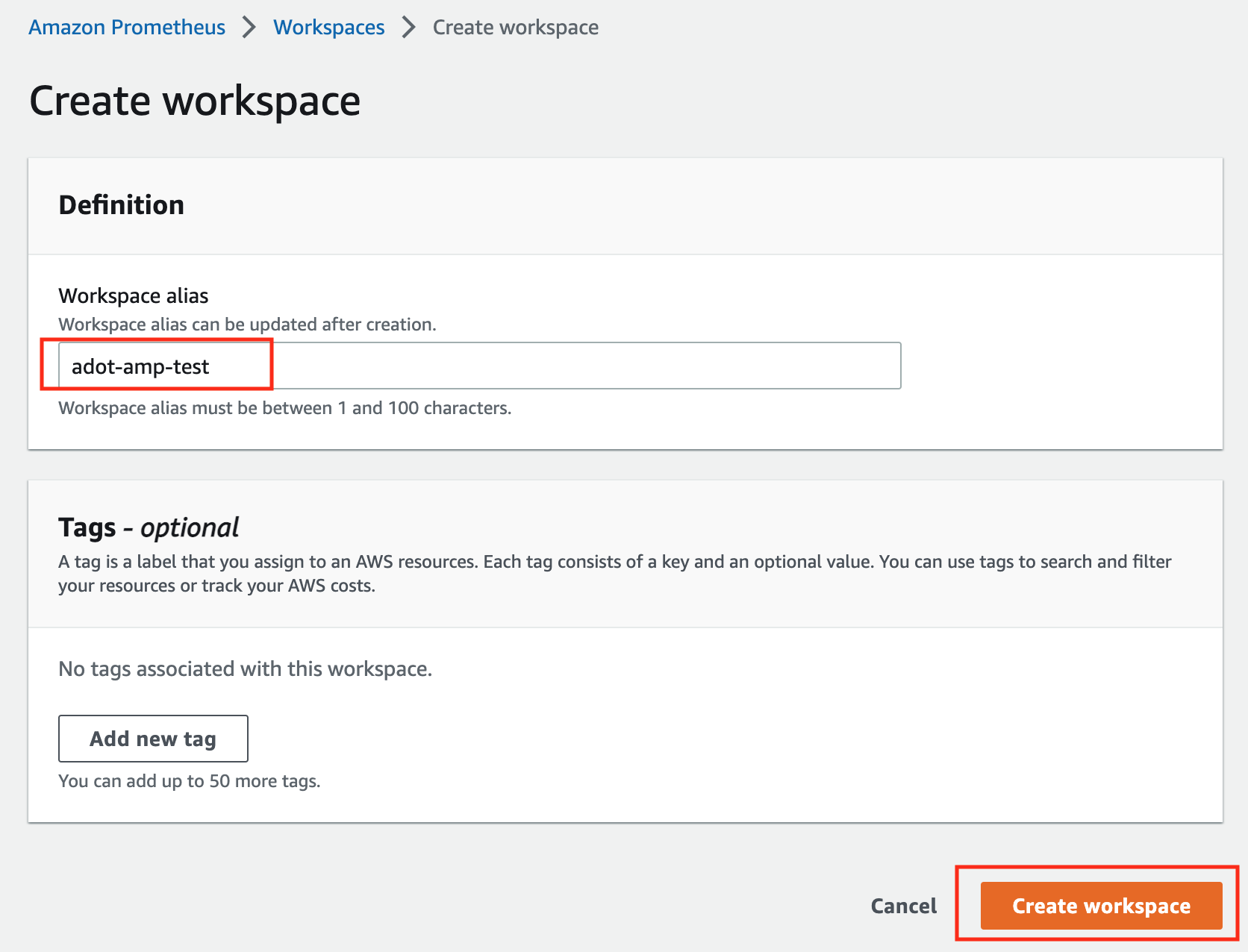
-
Make notes of the URLs displayed for Endpoint - remote write URL and Endpoint - query URL. You’ll need them when you configure your ADOT package to remote write metrics to this workspace and when you query metrics from this workspace. Make sure the workspace’s Status shows Active before proceeding to the next step.
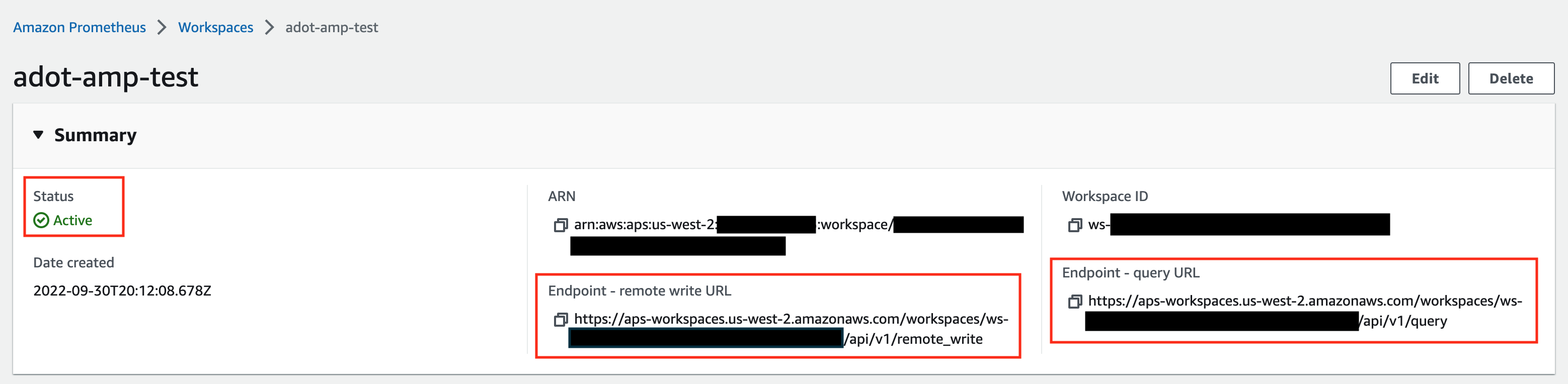
For additional options (i.e. through CLI) and configurations (i.e. add a tag) to create an AMP workspace, refer to AWS AMP create a workspace guide.
Create a cluster with IRSA
To enable ADOT pods that run in EKS Anywhere clusters to authenticate with AWS services, a user needs to set up IRSA at cluster creation. EKS Anywhere cluster spec for Pod IAM
gives step-by-step guidance on how to do so. There are a few things to keep in mind while working through the guide:
-
While completing step Create an OIDC provider
, a user should:
-
create the S3 bucket in the us-west-2 region, and
-
attach an IAM policy with proper AMP access to the IAM role.
Below is an example that gives full access to AMP actions and resources. Refer to AMP IAM permissions and policies guide
for more customized options.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"aps:*"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
-
While completing step deploy pod identity webhook
, a user should:
- make sure the service account is created in the same namespace as the ADOT package (which is controlled by the
package definition file with field spec.targetNamespace);
- take a note of the service account that gets created in this step as it will be used in ADOT package installation;
- add an annotation
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: <role-arn> to the created service account.
By default, the service account is installed in the default namespace with name pod-identity-webhook, and the annotation eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: <role-arn> is not added automatically.
IRSA Set Up Test
To ensure IRSA is set up properly in the cluster, a user can create an awscli pod for testing.
-
Apply the following yaml file in the cluster:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: awscli
spec:
serviceAccountName: pod-identity-webhook
containers:
- image: amazon/aws-cli
command:
- sleep
- "infinity"
name: awscli
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
EOF
-
Exec into the pod:
kubectl exec -it awscli -- /bin/bash
-
Check if the pod can list AMP workspaces:
aws amp list-workspaces --region=us-west-2
-
If the pod has issues listing AMP workspaces, re-visit IRSA set up guidance before proceeding to the next step.
-
Exit the pod:
exit
Install the ADOT package
The ADOT package will be created with three components:
-
the Prometheus Receiver, which is designed to be a drop-in replacement for a Prometheus Server and is capable of scraping metrics from microservices instrumented with the Prometheus client library
;
-
the Prometheus Remote Write Exporter, which employs the remote write features and send metrics to AMP for long term storage;
-
the Sigv4 Authentication Extension, which enables ADOT pods to authenticate to AWS services.
Follow steps below to complete the ADOT package installation:
-
Update the following config file. Review comments carefully and replace everything that is wrapped with a <> tag. Note this configuration aims to mimic the Prometheus community helm chart. A user can tailor the scrape targets further by modifying the receiver section below. Refer to ADOT package spec
for additional explanations of each section.
Click to expand ADOT package config
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: default # this needs to match the namespace of the serviceAccount below
config: |
mode: deployment
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: false
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# Specifies the serviceAccount annotated with eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn.
name: "pod-identity-webhook" # name of the service account created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
config:
extensions:
sigv4auth:
region: "us-west-2"
service: "aps"
assume_role:
sts_region: "us-west-2"
receivers:
# Scrape configuration for the Prometheus Receiver
prometheus:
config:
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: kubernetes-apiservers
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: default;kubernetes;https
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
- __meta_kubernetes_endpoint_port_name
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-nodes
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
target_label: __address__
- regex: (.+)
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$$1/proxy/metrics
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_node_name
target_label: __metrics_path__
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-nodes-cadvisor
bearer_token_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: node
relabel_configs:
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_node_label_(.+)
- replacement: kubernetes.default.svc:443
target_label: __address__
- regex: (.+)
replacement: /api/v1/nodes/$$1/proxy/metrics/cadvisor
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_node_name
target_label: __metrics_path__
scheme: https
tls_config:
ca_file: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/ca.crt
insecure_skip_verify: false
- job_name: kubernetes-service-endpoints
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name
target_label: kubernetes_node
- job_name: kubernetes-service-endpoints-slow
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: endpoints
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_node_name
target_label: kubernetes_node
scrape_interval: 5m
scrape_timeout: 30s
- job_name: prometheus-pushgateway
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: pushgateway
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe
- job_name: kubernetes-services
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: service
metrics_path: /probe
params:
module:
- http_2xx
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_annotation_prometheus_io_probe
- source_labels:
- __address__
target_label: __param_target
- replacement: blackbox
target_label: __address__
- source_labels:
- __param_target
target_label: instance
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_service_label_(.+)
- source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_service_name
target_label: kubernetes_name
- job_name: kubernetes-pods
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: kubernetes_namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_name
target_label: kubernetes_pod_name
- action: drop
regex: Pending|Succeeded|Failed|Completed
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_phase
- job_name: kubernetes-pods-slow
scrape_interval: 5m
scrape_timeout: 30s
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: keep
regex: true
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape_slow
- action: replace
regex: (https?)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scheme
target_label: __scheme__
- action: replace
regex: (.+)
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path
target_label: __metrics_path__
- action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $$1:$$2
source_labels:
- __address__
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port
target_label: __address__
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_param_(.+)
replacement: __param_$1
- action: labelmap
regex: __meta_kubernetes_pod_label_(.+)
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_namespace
target_label: namespace
- action: replace
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_name
target_label: pod
- action: drop
regex: Pending|Succeeded|Failed|Completed
source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_phase
processors:
batch/metrics:
timeout: 60s
exporters:
logging:
logLevel: info
prometheusremotewrite:
endpoint: "<AMP-WORKSPACE>/api/v1/remote_write" # Replace with your AMP workspace
auth:
authenticator: sigv4auth
service:
extensions:
- health_check
- memory_ballast
- sigv4auth
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
processors: [batch/metrics]
exporters: [logging, prometheusremotewrite]
-
Bind additional roles to the service account pod-identity-webhook (created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
) by applying the following file in the cluster (using kubectl apply -f <file-name>). This is because pod-identity-webhook by design does not have sufficient permissions to scrape all Kubernetes targets listed in the ADOT config file above. If modifications are made to the Prometheus Receiver, make updates to the file below to add / remove additional permissions before applying the file.
Click to expand clusterrole and clusterrolebinding config
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: otel-prometheus-role
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- nodes
- nodes/proxy
- services
- endpoints
- pods
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- nonResourceURLs:
- /metrics
verbs:
- get
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: otel-prometheus-role-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: otel-prometheus-role
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: pod-identity-webhook # replace with name of the service account created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
namespace: default # replace with namespace where the service account was created at step Create a cluster with IRSA
-
Use the ADOT package config file defined above to complete the ADOT installation. Refer to ADOT installation guide
for details.
ADOT Package Test
To ensure the ADOT package is installed correctly in the cluster, a user can perform the following tests.
Check pod logs
Check ADOT pod logs using kubectl logs <adot-pod-name> -n <namespace>. It should display logs similar to below.
...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.184Z info service/telemetry.go:103 Setting up own telemetry...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.184Z info service/telemetry.go:138 Serving Prometheus metrics {"address": "0.0.0.0:8888", "level": "basic"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.185Z info components/components.go:30 In development component. May change in the future. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging", "stability": "in development"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:42 Starting extensions...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info healthcheckextension@v0.58.0/healthcheckextension.go:44 Starting health_check extension {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check", "config": {"Endpoint":"0.0.0.0:13133","TLSSetting":null,"CORS":null,"Auth":null,"MaxRequestBodySize":0,"IncludeMetadata":false,"Path":"/","CheckCollectorPipeline":{"Enabled":false,"Interval":"5m","ExporterFailureThreshold":5}}}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.186Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info ballastextension/memory_ballast.go:52 Setting memory ballast {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast", "MiBs": 0}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "memory_ballast"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:45 Extension is starting... {"kind": "extension", "name": "sigv4auth"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info extensions/extensions.go:49 Extension started. {"kind": "extension", "name": "sigv4auth"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:74 Starting exporters...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:78 Exporter is starting... {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:82 Exporter started. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "logging"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:78 Exporter is starting... {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "prometheusremotewrite"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:82 Exporter started. {"kind": "exporter", "data_type": "metrics", "name": "prometheusremotewrite"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:86 Starting processors...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:90 Processor is starting... {"kind": "processor", "name": "batch/metrics", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:94 Processor started. {"kind": "processor", "name": "batch/metrics", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:98 Starting receivers...
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:102 Receiver is starting... {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.187Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.188Z info kubernetes/kubernetes.go:326 Using pod service account via in-cluster config {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics", "discovery": "kubernetes"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info pipelines/pipelines.go:106 Receiver started. {"kind": "receiver", "name": "prometheus", "pipeline": "metrics"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info healthcheck/handler.go:129 Health Check state change {"kind": "extension", "name": "health_check", "status": "ready"}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info service/collector.go:215 Starting aws-otel-collector... {"Version": "v0.21.1", "NumCPU": 2}
2022-09-30T23:22:59.189Z info service/collector.go:128 Everything is ready. Begin running and processing data.
...
Check AMP endpoint using awscurl
Use awscurl commands below to check if AMP received the metrics data sent by ADOT. The awscurl tool is a curl like tool with AWS Signature Version 4 request signing. The command below should return a status code success.
pip install awscurl
awscurl -X POST --region us-west-2 --service aps "<amp-query-endpoint>?query=up"
Create an AMG workspace and connect to the AMP workspace
An AMG workspace is created to query metrics from the AMP workspace and visualize the metrics in user-selected or user-built dashboards.
Follow steps below to create the AMG workspace:
-
Enable AWS Single-Sign-on (AWS SSO). Refer to IAM Identity Center
for details.
-
Open the Amazon Managed Grafana console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/grafana/.
-
Choose Create workspace.
-
In the Workspace details window, for Workspace name, enter a name for the workspace.
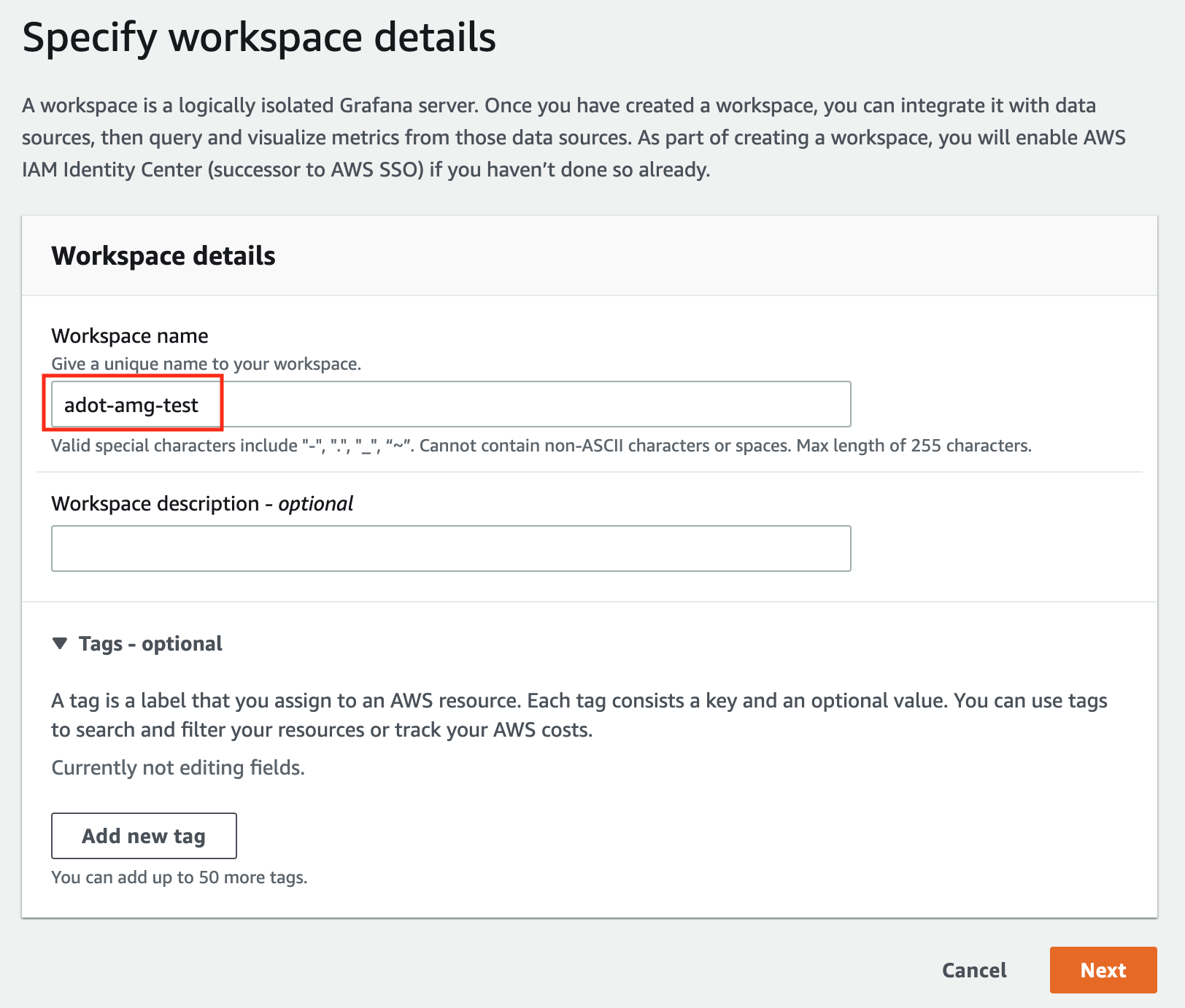
-
In the config settings window, choose Authentication access by AWS IAM Identity Center, and Permission type of Service managed.
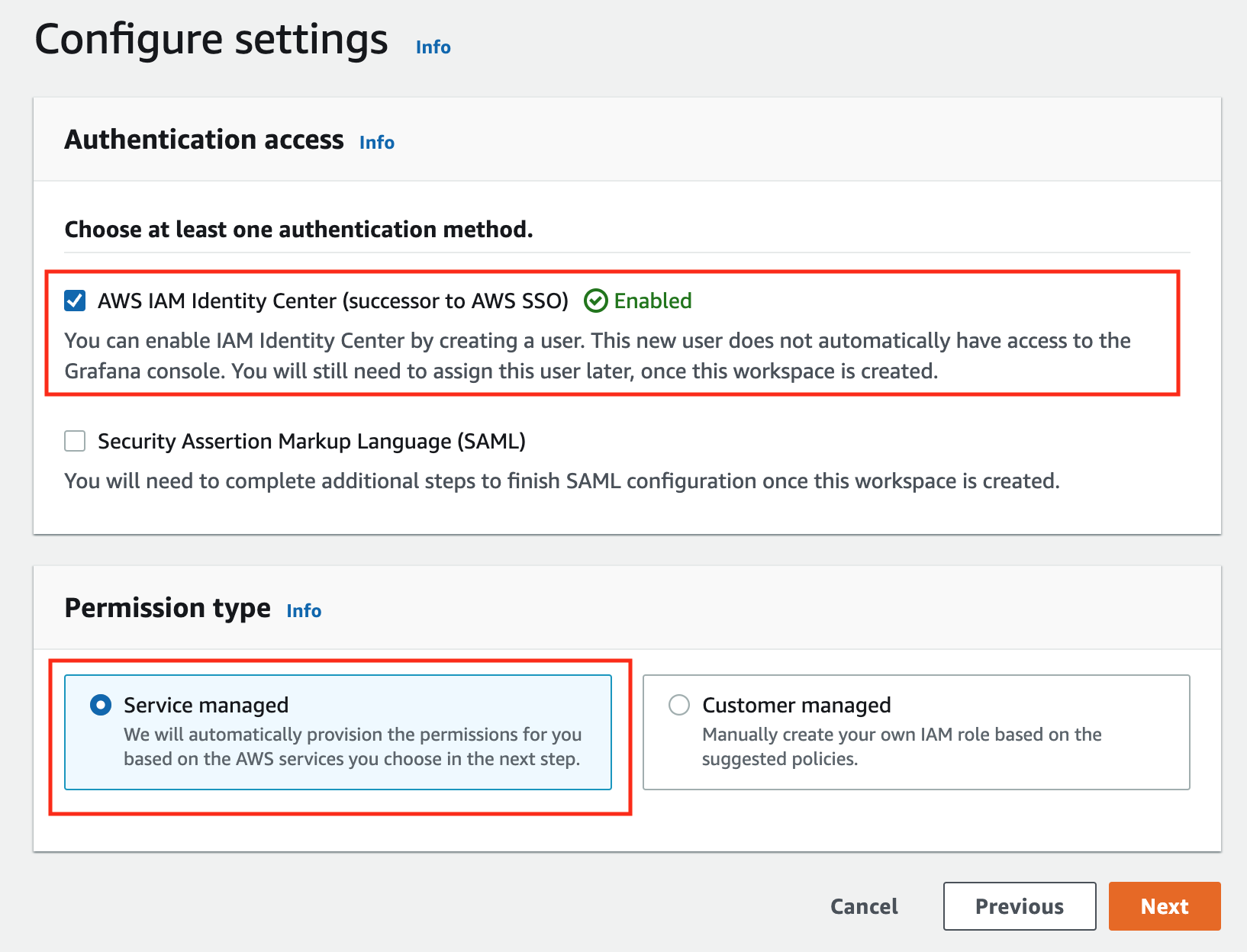
-
In the IAM permission access setting window, choose Current account access, and Amazon Managed Service for Prometheus as data source.
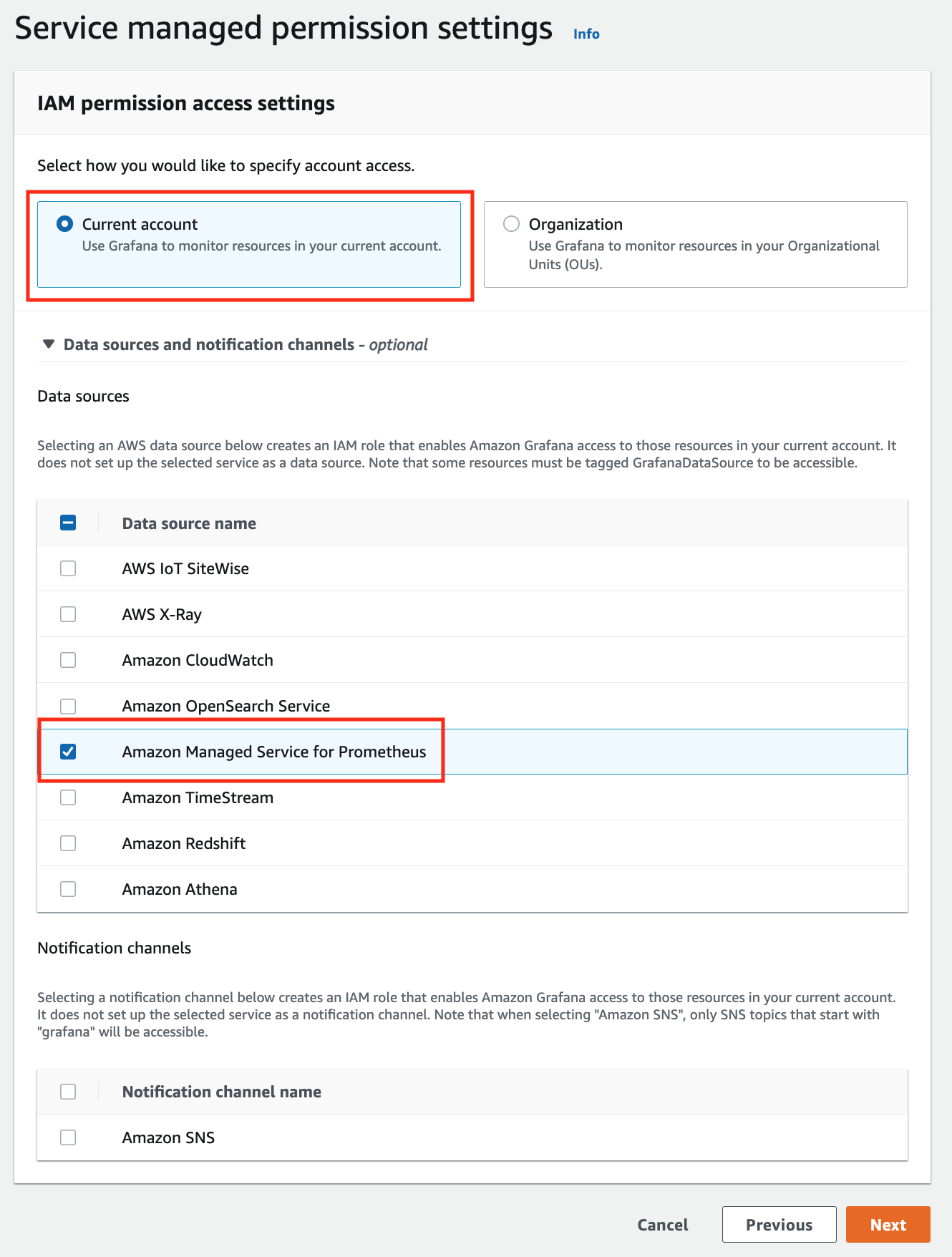
-
Review all settings and click on Create workspace.
-
Once the workspace shows a Status of Active, you can access it by clicking the Grafana workspace URL. Click on Sign in with AWS IAM Identity Center to finish the authentication.
Follow steps below to add the AMP workspace to AMG.
-
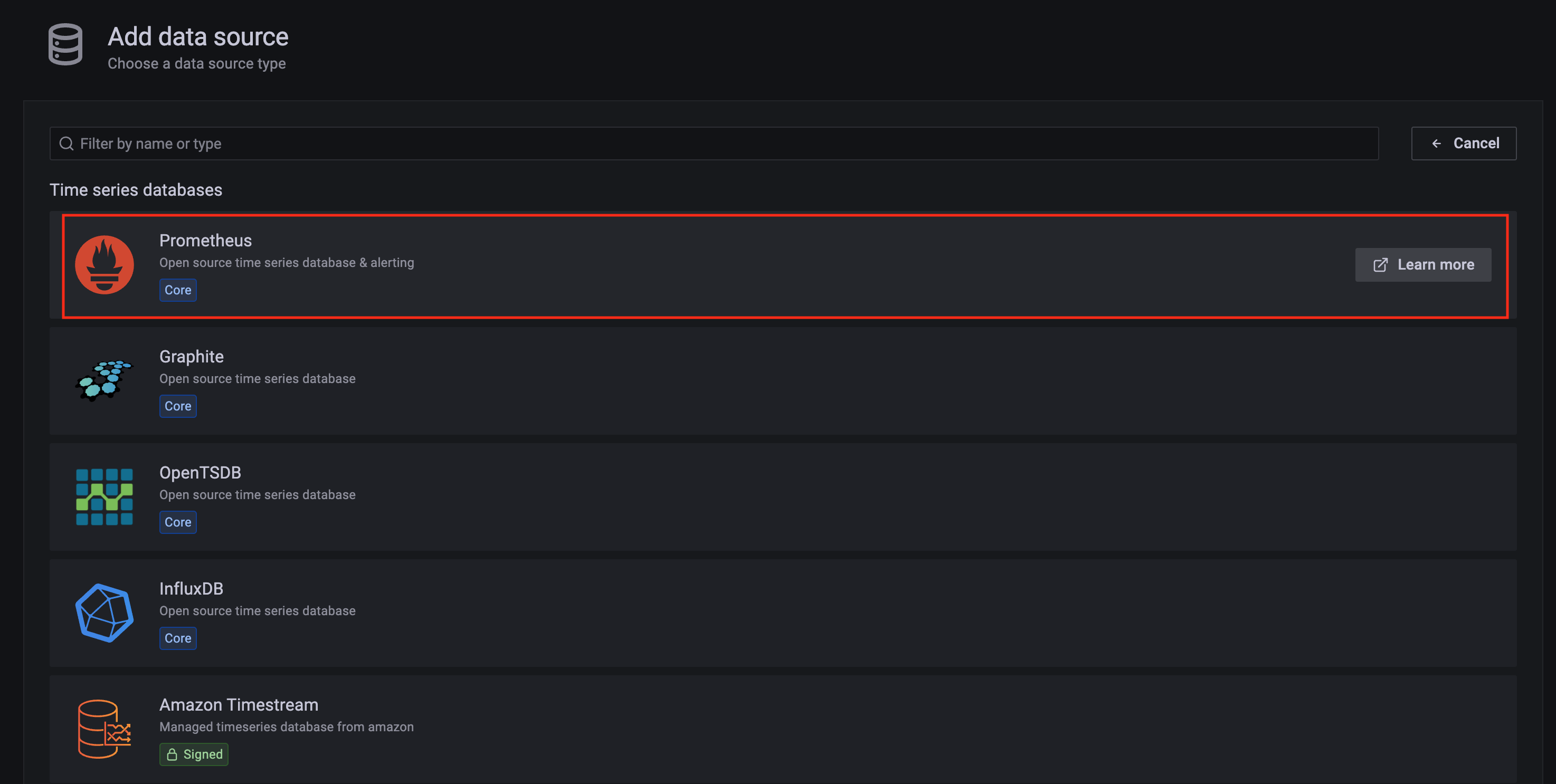
Click on the config sign on the left navigation bar, select Data sources, then choose Prometheus as the Data source.
-
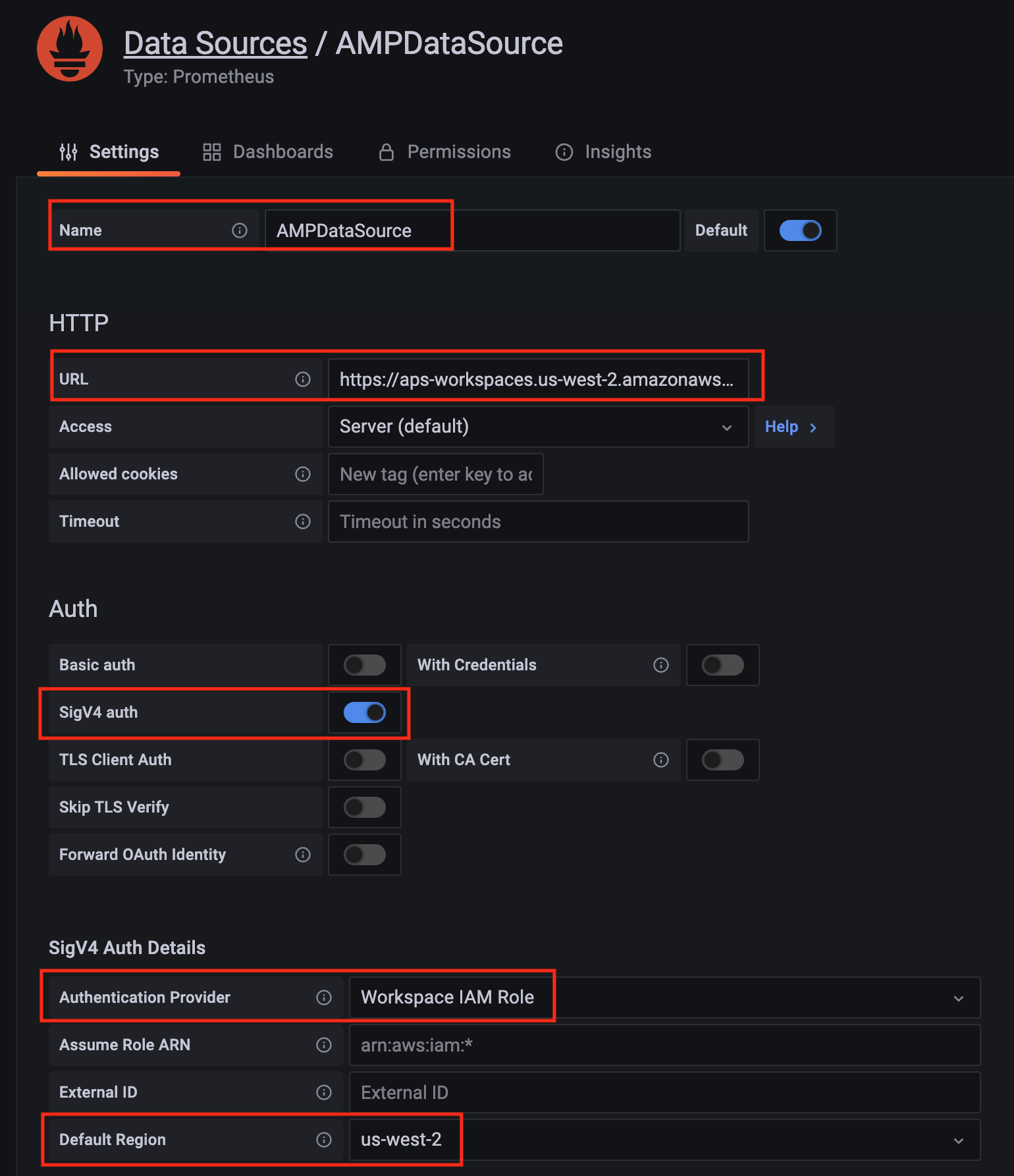
Configure Prometheus data source with the following details:
- Name:
AMPDataSource as an example.
- URL: add the AMP workspace remote write URL without the
api/v1/remote_write at the end.
- SigV4 auth: enable.
- Under the SigV4 Auth Details section:
- Authentication Provider: choose
Workspace IAM Role;
- Default Region: choose
us-west-2 (where you created the AMP workspace)
- Select the
Save and test, and a notification data source is working should be displayed.
-
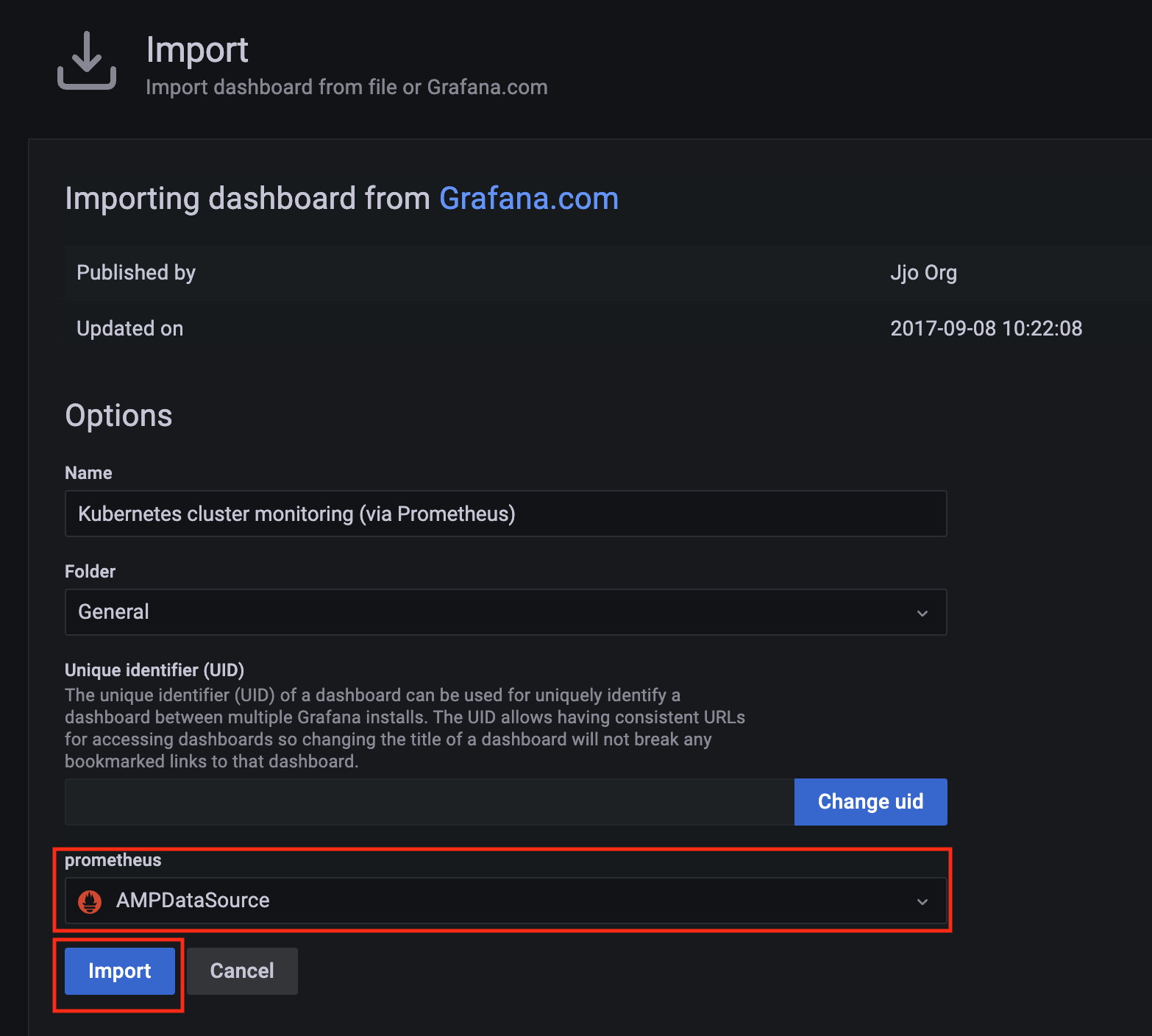
Import a dashboard template by clicking on the plus (+) sign on the left navigation bar. In the Import screen, type 3119 in the Import via grafana.com textbox and select Import.
From the dropdown at the bottom, select AMPDataSource and select Import.
-
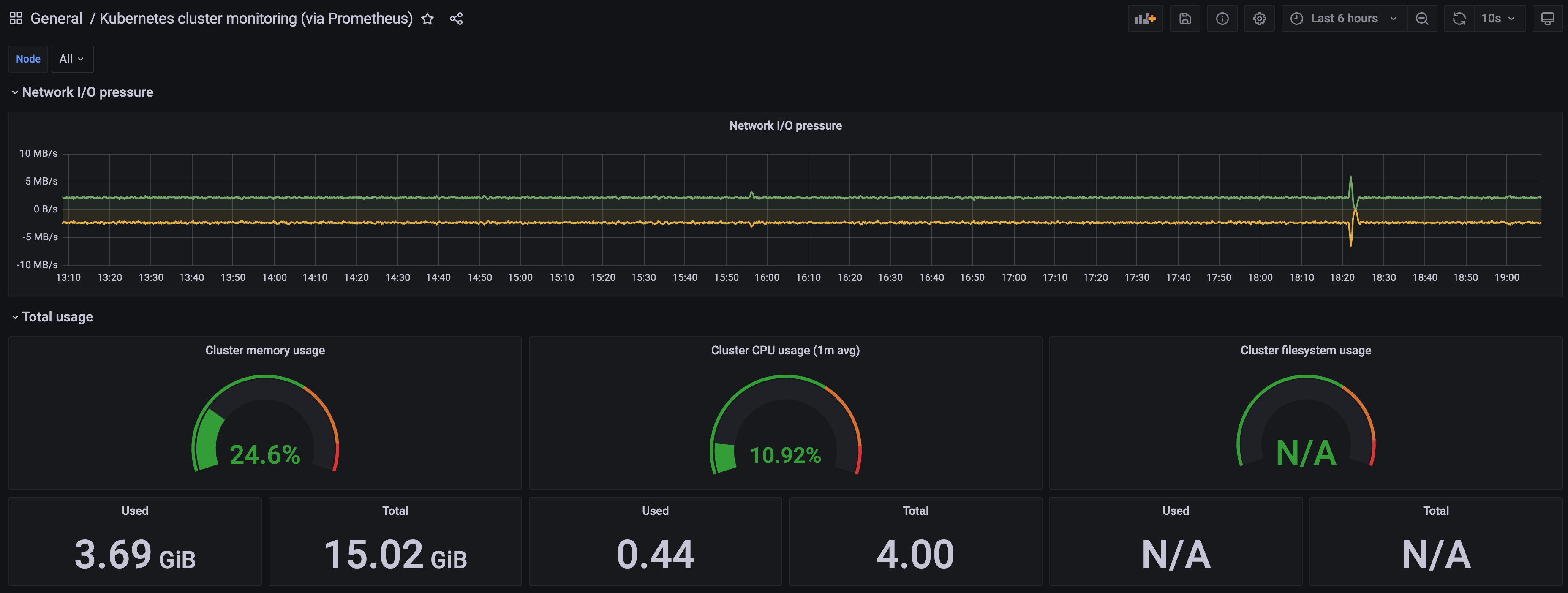
A Kubernetes cluster monitoring (via Prometheus) dashboard will be displayed.
10.2 - AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT)
Install/upgrade/uninstall ADOT
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package adot --cluster <cluster-name> > adot.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to adot.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file with daemonSet mode and default configuration:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Example package file with deployment mode and customized collector components to scrap
ADOT collector’s own metrics:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: deployment
replicaCount: 2
config:
receivers:
prometheus:
config:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: opentelemetry-collector
scrape_interval: 10s
static_configs:
- targets:
- ${MY_POD_IP}:8888
processors:
batch: {}
memory_limiter: null
exporters:
logging:
loglevel: debug
prometheusremotewrite:
endpoint: "<prometheus-remote-write-end-point>"
extensions:
health_check: {}
memory_ballast: {}
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [prometheus]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [logging, prometheusremotewrite]
telemetry:
metrics:
address: 0.0.0.0:8888
-
Create the namespace
(If overriding targetNamespace, change observability to the value of targetNamespace)
kubectl create namespace observability
-
Install adot
eksctl anywhere create packages -f adot.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
my-adot adot 19h installed 0.25.0-c26690f90d38811dbb0e3dad5aea77d1efa52c7b 0.25.0-c26690f90d38811dbb0e3dad5aea77d1efa52c7b (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update adot.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f adot.yaml
Upgrade
ADOT will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall ADOT, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> my-adot
10.3 - v0.21.1
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
10.4 - v0.23.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
10.5 - v0.25.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
10.6 - v0.39.0
Configuring ADOT in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
We included a sample configuration below for reference. For in-depth examples and use cases, please refer to ADOT with AMP and AMG.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-adot
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: adot
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
mode: daemonset
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Indicates if the pod should run in the host networking namespace. |
false |
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| mode |
Specifies Collector deployment options: daemonset, deployment, or statefulset. |
"daemonset" |
| ports.[*].containerPort |
Specifies containerPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].enabled |
Indicates if a port is enabled. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].hostPort |
Specifies hostPort used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].protocol |
Specifies protocol used. |
See footnote |
| ports.[*].servicePort |
Specifies servicePort used. |
See footnote |
| resources.limits.cpu |
Specifies CPU resource limits for containers. |
1 |
| resources.limits.memory |
Specifies memory resource limits for containers. |
"2Gi" |
| Config |
|
|
| config.config |
Specifies Collector receiver, processor, exporter, and extensions configurations. Refer to aws-otel-collector
for full details. Note EKS Anywhere ADOT package version matches the exact aws-otel-collector version. |
See footnote |
| config.config.receiver |
Specifies how data gets in the Collector. Receivers can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.processor |
Specifies how processors are run on data between the stage of being received and being exported. Processors are optional though some are recommended.
|
See footnote |
| config.config.exporters |
Specifies how data gets sent to backends/destinations. Exporters can be either push or pull based, and support one or more data source. |
See footnote |
| config.config.extensions |
Specifies tasks that do not involve processing telemetry data. Examples of extensions include health monitoring, service discovery, and data forwarding. Extensions are optional. |
See footnote |
| config.config.service |
Specifies what components are enabled in the Collector based on the configuration found in the receivers, processors, exporters, and extensions sections. If a component is configured, but not defined within the service section, then it is not enabled. |
See footnote |
| Deployment mode only |
|
|
| replicaCount |
Specifies replicaCount for pods. |
1 |
| service.type |
Specifies service types: ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName. |
"ClusterIP" |
11 - Cert-Manager Configuration
The cert-manager package adds certificates and certificate issuers as resource types in Kubernetes clusters, and simplifies the process of obtaining, renewing and using those certificates.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for Cert-Manager
11.1 - Cert-Manager
Install/update/upgrade/uninstall Cert-Manager
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install on workload cluster
NOTE: The cert-manager package can only be installed on a workload cluster
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package cert-manager --cluster <cluster-name> > cert-manager.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to cert-manager.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file configuring a cert-manager package to run on a workload cluster.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-cert-manager
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: cert-manager
targetNamespace: <namespace-to-install-component>
-
Install Cert-Manager
eksctl anywhere create packages -f cert-manager.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
my-cert-manager cert-manager 15s installed 1.9.1-dc0c845b5f71bea6869efccd3ca3f2dd11b5c95f 1.9.1-dc0c845b5f71bea6869efccd3ca3f2dd11b5c95f (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update cert-manager.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f cert-manager.yaml
Upgrade
Cert-Manager will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall cert-manager, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> cert-manager
11.2 - v1.14.5
Configuring Cert-Manager in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-cert-manager
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: cert-manager
config: |
global:
logLevel: 4
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the cert-manager package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
namespace |
The namespace to use for installing cert-manager package |
cert-manager |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
| global |
|
|
global.logLevel |
The log level: integer from 0-6 |
2 |
| Webhook |
|
|
webhook.timeoutSeconds |
The time in seconds to wait for the webhook to connect with the kube-api server |
0 |
11.3 - v1.9.1
Configuring Cert-Manager in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-cert-manager
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: cert-manager
config: |
global:
logLevel: 4
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the cert-manager package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
namespace |
The namespace to use for installing cert-manager package |
cert-manager |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
| global |
|
|
global.logLevel |
The log level: integer from 0-6 |
2 |
| Webhook |
|
|
webhook.timeoutSeconds |
The time in seconds to wait for the webhook to connect with the kube-api server |
0 |
12 - Cluster Autoscaler Configuration
Cluster Autoscaler is a component that automatically adjusts the size of a Kubernetes Cluster so that all pods have a place to run and there are no unneeded nodes.
Configuration options for Cluster Autoscaler
12.1 - Cluster Autoscaler
Install/upgrade/uninstall Cluster Autoscaler
If you have not already done so, make sure your EKS Anywhere cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Enable Cluster Autoscaling
-
Ensure you have configured at least one worker node group in your cluster specification to enable autoscaling as outlined in Autoscaling configuration.
Cluster Autoscaler only works on node groups with an autoscalingConfiguration set:
apiVersion: anywhere.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: <cluster-name>
spec:
...
workerNodeGroupConfigurations:
- autoscalingConfiguration:
minCount: 1
maxCount: 5
machineGroupRef:
kind: VSphereMachineConfig
name: <worker-machine-config-name>
count: 1
name: md-0
-
Generate the package configuration.
eksctl anywhere generate package cluster-autoscaler --cluster <cluster-name> > cluster-autoscaler.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to cluster-autoscaler.yaml. See configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values. See below for an example package file configuring a Cluster Autoscaler package.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: cluster-autoscaler-<cluster-name>
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: cluster-autoscaler
targetNamespace: default
config: |-
cloudProvider: "clusterapi"
autoDiscovery:
clusterName: "<cluster-name>"
-
Install Cluster Autoscaler
eksctl anywhere create packages -f cluster-autoscaler.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
NAMESPACE NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
eksa-packages-mgmt-v-vmc cluster-autoscaler cluster-autoscaler 18h installed 9.21.0-1.21-147e2a701f6ab625452fe311d5c94a167270f365 9.21.0-1.21-147e2a701f6ab625452fe311d5c94a167270f365 (latest)
To verify that autoscaling works, apply the deployment below. You must continue scaling pods until the deployment has pods in a pending state.
This is when Cluster Autoscaler will begin to autoscale your machine deployment.
This process may take a few minutes.
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aws/eks-anywhere/d8575bbd2a85a6c6bbcb1a54868cf7790df56a63/test/framework/testdata/hpa_busybox.yaml
kubectl scale deployment hpa-busybox-test --replicas 100
Update
To update package configuration, update the cluster-autoscaler.yaml file and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f cluster-autoscaler.yaml
Update Worker Node Group Autoscaling Configuration
It is possible to change the autoscaling configuration of a worker node group by updating the autoscalingConfiguration in your cluster specification and running a cluster upgrade.
Upgrade
The Cluster Autoscaler can be upgraded by PackageController’s activeBundle field to a newer version.
The curated packages bundle contains the SHAs of the images and helm charts associated with a particular package. When a new version is activated, the Package Controller will reconcile all active packages to their newest versions as defined in the bundle.
The Curated Packages Controller automatically polls the bundle repository for new bundle resources.
The curated packages controller automatically polls for the latest bundle, but requires the activeBundle field on the PackageController resource to be updated before a new bundle will take effect and upgrade the resources.
Uninstall
To uninstall Cluster Autoscaler, delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> cluster-autoscaler
12.2 - v9.21.0
Configuring Cluster Autoscaler in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| cloudProvider |
Cluster Autoscaler cloud provider. This should always be clusterapi.
Example:
cloudProvider: “clusterapi” |
“clusterapi” |
| autoDiscovery.clusterName |
Name of the kubernetes cluster this autoscaler package should autoscale.
Example:
autoDiscovery.clusterName: “mgmt-cluster” |
false |
| clusterAPIMode |
Where Cluster Autoscaler should look for a kubeconfig to communicate with the cluster it will manage. See https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/clusterapi/README.md#connecting-cluster-autoscaler-to-cluster-api-management-and-workload-clusters
Example:
clusterAPIMode: “incluster-kubeconfig” |
“incluster-incluster” |
| clusterAPICloudConfigPath |
Path to kubeconfig for connecting to Cluster API Management Cluster, only used if clusterAPIMode=kubeconfig-kubeconfig or incluster-kubeconfig
Example:
clusterAPICloudConfigPath: “/etc/kubernetes/value” |
“/etc/kubernetes/mgmt-kubeconfig” |
| extraVolumeSecrets |
Additional volumes to mount from Secrets.
Example:
extraVolumeSecrets: {} |
{} |
12.3 - v9.37.0
Configuring Cluster Autoscaler in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| cloudProvider |
Cluster Autoscaler cloud provider. This should always be clusterapi.
Example:
cloudProvider: “clusterapi” |
“clusterapi” |
| autoDiscovery.clusterName |
Name of the kubernetes cluster this autoscaler package should autoscale.
Example:
autoDiscovery.clusterName: “mgmt-cluster” |
false |
| clusterAPIMode |
Where Cluster Autoscaler should look for a kubeconfig to communicate with the cluster it will manage. See https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/blob/master/cluster-autoscaler/cloudprovider/clusterapi/README.md#connecting-cluster-autoscaler-to-cluster-api-management-and-workload-clusters
Example:
clusterAPIMode: “incluster-kubeconfig” |
“incluster-incluster” |
| clusterAPICloudConfigPath |
Path to kubeconfig for connecting to Cluster API Management Cluster, only used if clusterAPIMode=kubeconfig-kubeconfig or incluster-kubeconfig
Example:
clusterAPICloudConfigPath: “/etc/kubernetes/value” |
“/etc/kubernetes/mgmt-kubeconfig” |
| extraVolumeSecrets |
Additional volumes to mount from Secrets.
Example:
extraVolumeSecrets: {} |
{} |
13 - Credential Provider Package Configuration
Credential provider package provides a solution to authenticate with private Amazon Elastic Container Registry by utilizing the kubelet image credential provider
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for Credential-Provider-Package
13.1 - Credential Provider Package with IAM Roles Anywhere
This tutorial demonstrates how to configure the credential provider package to authenticate using IAM Roles Anywhere
to pull from a private AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR).
IAM Roles Anywhere enables workloads outside of AWS to access AWS resources by using X.509 digital certificates to obtain temporary AWS credentials. A trust anchor is used to reference a certificate authority with IAM Roles Anywhere. For this use case, the Kubernetes Cluster CA can be registered and each kubelet client’s x509 cert can be used to authenticate to get temporary AWS credentials.
Prerequisites
-
For setting up the certificate authority later, you will need to obtain your cluster’s CA. This can be obtain by:
# Assuming CLUSTER_NAME and KUBECONFIG are set:
kubectl get secret -n eksa-system ${CLUSTER_NAME}-ca -o yaml | yq '.data."tls.crt"' | base64 -d
-
A role should be created to allow read access for curated packages. This role can be extended to include private registries that you would also like to pull from into your cluster. A sample policy for curated packages would be.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "ECRRead",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:DescribeImageScanFindings",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:DescribeRegistry",
"ecr:DescribePullThroughCacheRules",
"ecr:DescribeImageReplicationStatus",
"ecr:ListTagsForResource",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:DescribeImages",
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:ecr:*:783794618700:repository/*"
},
{
"Sid": "ECRLogin",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
-
Next create a trust anchor and profile. The trust anchor will be a reference to the CA certificate from step 1 and the profile should point to the role created in step 2. See here
for instructions on creating the trust anchor and profile.
-
Create a secret that will be referenced by the credential-provider-package to authenticate the kubelet with ECR.
# Set PROFILE_ARN, ROLE_ARN, and TRUST_ANCHOR_ARN obtained in previous step
# Set AWS_REGION to region to pull images from
# This will create a file credfile which will then be turned into a secret
cat << EOF >> credfile
[default]
region = $AWS_REGION
credential_process = aws_signing_helper credential-process --certificate /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem --private-key /var/lib/kubelet/pki/kubelet-client-current.pem --profile-arn $PROFILE_ARN --role-arn $ROLE_ARN --trust-anchor-arn $TRUST_ANCHOR_ARN
EOF
# Create secret, for this example the secret name aws-config is used and the package will be installed in eksa-packages
kubectl create secret generic aws-config --from-file=config=credfile -n eksa-packages
-
Either edit the existing package or delete and create a new credential-provider-package that points towards the new secret. For more information on specific configuration option refer to installation guide
for details]
The example below changes the default secret name from aws-secret to newly created aws-config. It also changes the match images to pull from multiple regions as well as across multiple accounts. Make sure to change cluster-name to match your CLUSTER_NAME
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-credential-provider-package
namespace: eksa-packages-<clusterName>
annotations:
"helm.sh/resource-policy": keep
"anywhere.eks.aws.com/internal": "true"
spec:
packageName: credential-provider-package
targetNamespace: eksa-packages
config: |-
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
sourceRegistry: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
credential:
- matchImages:
- *.dkr.ecr.*.amazonaws.com
profile: "default"
secretName: aws-config
defaultCacheDuration: "5h"
13.2 - Credential Provider Package
Install/upgrade/uninstall Credential Provider Package
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
By default an instance of this package is installed with the controller to help facilitate authentication for other packages. The following are instructions in case you want to tweak the default values.
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package credential-provider-package --cluster <cluster-name> > credential-provider-package.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to credential-provider-package.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example default package using IAM User Credentials installed with the controller
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-credential-provider-package
namespace: eksa-packages-<clusterName>
annotations:
"helm.sh/resource-policy": keep
"anywhere.eks.aws.com/internal": "true"
spec:
packageName: credential-provider-package
targetNamespace: eksa-packages
config: |-
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
sourceRegistry: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
credential:
- matchImages:
- 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
profile: "default"
secretName: aws-secret
defaultCacheDuration: "5h"
-
Create the secret. If you are changing the secret, see complete configuration options
for the format of the secret.
-
Create the namespace (if not installing to eksa-packages).
If you are overriding targetNamespace, change eksa-packages to the value of targetNamespace.
kubectl create namespace <namespace-name-here>
-
Install the credential-provider-package
eksctl anywhere create packages -f credential-provider-package.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Update
To update package configuration, update credential-provider-package.yaml file and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f credential-provider-package.yaml
Upgrade
Credential-Provider-Package will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall credential-provider-package, simply delete the package:
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> my-credential-provider-package
13.3 - v0.1.0
Configuring Credential Provider Package in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
The following is the sample configuration for the credential provider package that is installed by default with the package controller.
Please refer to Credential Provider Package with IAM Roles Anywhere.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: ecr-credential-provider-package
namespace: eksa-packages-<clusterName>
annotations:
"helm.sh/resource-policy": keep
"anywhere.eks.aws.com/internal": "true"
spec:
packageName: credential-provider-package
targetNamespace: eksa-packages
config: |-
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
sourceRegistry: public.ecr.aws/eks-anywhere
credential:
- matchImages:
- 783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com
profile: "default"
secretName: aws-secret
defaultCacheDuration: "5h"
In this example, the credential provider will use the secret provided in aws-secret (created automatically on cluster creation) to authenticate to the repository from which curated package images are pulled. Tolerations were also added so that the control plane nodes would also be configured with authentication.
The secret can exist in two forms: either a base64 encoding of a credential config or individual keys for fields.
Example credential
[default]
aws_access_key_id=EXAMPLE_ACCESS_KEY
aws_secret_access_key=EXAMPLE_SECRET_KEY
region=us-west-2
Example secret with separate keys
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-secret
namespace: eksa-packages
data:
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: "QUtJQUlPU0ZPRE5ON0VYQU1QTEUK"
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: "d0phbHJYVXRuRkVNSS9LN01ERU5HL2JQeFJmaUNZRVhBTVBMRUtFWQo="
REGION: dXMtd2VzdC0yCg==
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-secret
namespace: eksa-packages
data:
config: W2RlZmF1bHRdCmF3c19hY2Nlc3Nfa2V5X2lkPUFLSUFJT1NGT0ROTjdFWEFNUExFCmF3c19zZWNyZXRfYWNjZXNzX2tleT13SmFsclhVdG5GRU1JL0s3TURFTkcvYlB4UmZpQ1lFWEFNUExFS0VZCnJlZ2lvbj11cy13ZXN0LTI=
type: Opaque
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| image.pullPolicy |
Specifies image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never. |
"IfNotPresent" |
| tolerations |
Kubernetes tolerations
for pod scheduling |
{} |
| Credential |
|
|
| credential |
List of credential providers for authenticating with ECR. Currently only one is supported |
credential:
- secretName: “aws-secret”
matchImages: []
defaultCacheDuration: “1h”
profile: “default |
| secretName |
Name of secret that contains the aws credentials |
"aws-secret" |
| profile |
AWS Profile for secretName |
"default" |
| matchImages |
List of strings used to match against images. See here
for more info
Example to match against any account across multiple regions for ECR:
"*.dkr.ecr.*.amazonaws.com" |
"[]" |
| defaultCacheDuration |
Duration the kubelet will cache credentials in-memory. For ECR it is recommended to keep this value less then 12 hours. |
"5h" |
14 - Emissary Configuration
Emissary Ingress is an open-source Kubernetes-native API Gateway + Layer 7 load balancer + Kubernetes Ingress built on Envoy Proxy.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for Emissary
14.1 - Emissary Ingress
Install/upgrade/uninstall Emissary Ingress
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package emissary --cluster <cluster-name> > emissary.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to emissary.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file with standard configuration.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: emissary
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: emissary
-
Install Emissary
eksctl anywhere create packages -f emissary.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAMESPACE NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
eksa-packages emissary emissary 2m57s installed 3.0.0-a507e09c2a92c83d65737835f6bac03b9b341467 3.0.0-a507e09c2a92c83d65737835f6bac03b9b341467 (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update emissary.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f emissary.yaml
Upgrade
Emissary will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall Emissary, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> emissary
14.2 - v3.0.0
Configuring Emissary Ingress in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Whether Emissary will use the host network, useful for on-premise setup .
Example:
hostNetwork: false |
false |
| createDefaultListeners |
Whether Emissary should be created with default listeners, HTTP on port 8080 and HTTPS on port 8443.
Example:
createDefaultListeners: false |
false |
| replicaCount |
Replica count for Emissary to deploy.
Example:
replicaCount: 2 |
2 |
| daemonSet |
Whether to create Emissary as a Daemonset instead of a deployment
Example:
daemonSet: false |
false |
14.3 - v3.3.0
Emissary version 0.3.3 has decoupled the CRD portion of the package, and now supports installing multiple instances of the emissary package in the same cluster.
Configuring Emissary Ingress in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Whether Emissary will use the host network, useful for on-premise setup .
Example:
hostNetwork: false |
false |
| createDefaultListeners |
Whether Emissary should be created with default listeners, HTTP on port 8080 and HTTPS on port 8443.
Example:
createDefaultListeners: false |
false |
| replicaCount |
Replica count for Emissary to deploy.
Example:
replicaCount: 2 |
2 |
| daemonSet |
Whether to create Emissary as a Daemonset instead of a deployment
Example:
daemonSet: false |
false |
14.4 - v3.9.1
Emissary version 3.9.1 has decoupled the CRD portion of the package, and now supports installing multiple instances of the emissary package in the same cluster.
Configuring Emissary Ingress in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| hostNetwork |
Whether Emissary will use the host network, useful for on-premise setup .
Example:
hostNetwork: false |
false |
| createDefaultListeners |
Whether Emissary should be created with default listeners, HTTP on port 8080 and HTTPS on port 8443.
Example:
createDefaultListeners: false |
false |
| replicaCount |
Replica count for Emissary to deploy.
Example:
replicaCount: 2 |
2 |
| daemonSet |
Whether to create Emissary as a Daemonset instead of a deployment
Example:
daemonSet: false |
false |
15 - Harbor Configuration
Harbor
is an open source trusted cloud native registry project that stores, signs, and scans content. Harbor extends the open source Docker Distribution by adding the functionalities usually required by users such as security, identity and management. Having a registry closer to the build and run environment can improve the image transfer efficiency. Harbor supports replication of images between registries, and also offers advanced security features such as user management, access control and activity auditing. For EKS Anywhere deployments, common use cases for Harbor include:
- Supporting Airgapped
environments.
- Running a registry mirror
that is closer to the build and run environment to improve the image transfer efficiency.
- Following any company policies around image locality.
For additional Harbor use cases see Harbor use cases
.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for Harbor
15.1 - Harbor
Install/upgrade/uninstall Harbor
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Set the KUBECONFIG environment variable to use the config of the management cluster
export KUBECONFIG=<path to management cluster kubeconfig>
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package harbor --cluster <cluster-name> > harbor.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to harbor.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Important
- All configuration options are listed in dot notations (e.g.,
expose.tls.enabled) in the doc, but they have to be transformed to hierachical structures when specified in the config section in the YAML spec.
- Harbor web portal is exposed through
NodePort by default, and its default port number is 30003 with TLS enabled and 30002 with TLS disabled.
- TLS is enabled by default for connections to Harbor web portal, and a secret resource named
harbor-tls-secret is required for that purpose. It can be provisioned through cert-manager or manually with the following command using self-signed certificate:
kubectl create secret tls harbor-tls-secret --cert=[path to certificate file] --key=[path to key file] -n eksa-packages
secretKey has to be set as a string of 16 characters for encryption.
TLS example with auto certificate generation
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-harbor
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: harbor
config: |-
secretKey: "use-a-secret-key"
externalURL: https://harbor.eksa.demo:30003
expose:
tls:
certSource: auto
auto:
commonName: "harbor.eksa.demo"
Non-TLS example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-harbor
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: harbor
config: |-
secretKey: "use-a-secret-key"
externalURL: http://harbor.eksa.demo:30002
expose:
tls:
enabled: false
-
Install Harbor
eksctl anywhere create packages -f harbor.yaml
-
Check Harbor
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
my-harbor harbor 5m34s installed v2.5.1 v2.5.1 (latest)
Harbor web portal is accessible at whatever externalURL is set to. See complete configuration options
for all default values.
Update
To update package configuration, update harbor.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f harbor.yaml
Upgrade
Note
- New versions of software packages will be automatically downloaded but not automatically installed. You can always manually run
eksctl to check and install updates.
-
Verify a new bundle is available
eksctl anywhere get packagebundle
Example command output
NAME VERSION STATE
v1.25-120 1.25 active (upgrade available)
v1.26-120 1.26 inactive
-
Upgrade Harbor
eksctl anywhere upgrade packages --bundle-version v1.26-120
-
Check Harbor
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
my-harbor Harbor 14m installed v2.7.1 v2.7.1 (latest)
Uninstall
-
Uninstall Harbor
Important
- By default, PVCs created for jobservice and registry are not removed during a package delete operation, which can be changed by leaving
persistence.resourcePolicy empty.
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> my-harbor
15.2 - Harbor use cases
Try some harbor use cases
Proxy a public Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) repository
This use case is to use Harbor to proxy and cache images from a public ECR repository, which helps limit the amount of requests made to a public ECR repository, avoiding consuming too much bandwidth or being throttled by the registry server.
-
Login
Log in to the Harbor web portal with the default credential as shown below

-
Create a registry proxy
Navigate to Registries on the left panel, and then click on NEW ENDPOINT button. Choose Docker Registry as the Provider, and enter public-ecr as the Name, and enter https://public.ecr.aws/ as the Endpoint URL. Save it by clicking on OK.
-
Create a proxy project
Navigate to Projects on the left panel and click on the NEW PROJECT button. Enter proxy-project as the Project Name, check Public access level, and turn on Proxy Cache and choose public-ecr from the pull-down list. Save the configuration by clicking on OK.
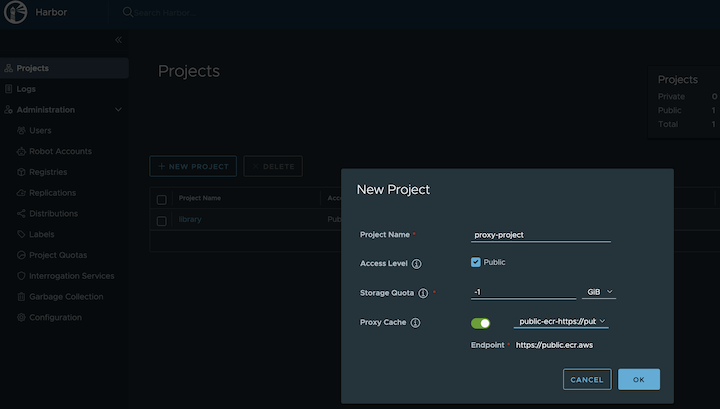
-
Pull images
Note
harbor.eksa.demo:30003 should be replaced with whatever externalURL is set to in the Harbor package YAML file.
docker pull harbor.eksa.demo:30003/proxy-project/cloudwatch-agent/cloudwatch-agent:latest
Proxy a private Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) repository
This use case is to use Harbor to proxy and cache images from a private ECR repository, which helps limit the amount of requests made to a private ECR repository, avoiding consuming too much bandwidth or being throttled by the registry server.
-
Login
Log in to the Harbor web portal with the default credential as shown below

-
Create a registry proxy
In order for Harbor to proxy a remote private ECR registry, an IAM credential with necessary permissions need to be created. Usually, it follows three steps:
-
Policy
This is where you specify all necessary permissions. Please refer to private repository policies
, IAM permissions for pushing an image
and ECR policy examples
to figure out the minimal set of required permissions.
For simplicity, the build-in policy AdministratorAccess is used here.
-
User group
This is an easy way to manage a pool of users who share the same set of permissions by attaching the policy to the group.
-
User
Create a user and add it to the user group. In addition, please navigate to Security credentials to generate an access key. Access keys consists of two parts: an access key ID and a secret access key. Please save both as they are used in the next step.
Navigate to Registries on the left panel, and then click on NEW ENDPOINT button. Choose Aws ECR as Provider, and enter private-ecr as Name, https://[ACCOUNT NUMBER].dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/ as Endpoint URL, use the access key ID part of the generated access key as Access ID, and use the secret access key part of the generated access key as Access Secret. Save it by click on OK.
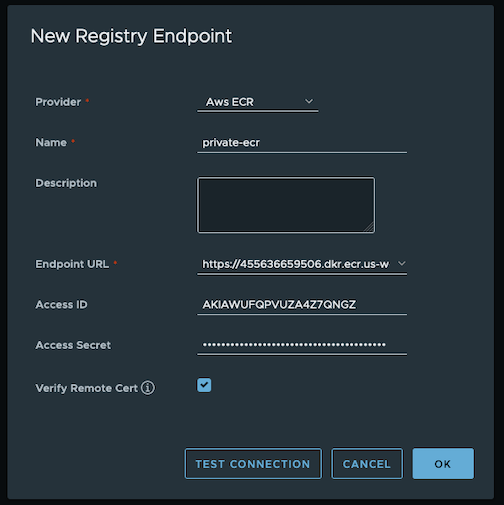
-
Create a proxy project
Navigate to Projects on the left panel and click on NEW PROJECT button. Enter proxy-private-project as Project Name, check Public access level, and turn on Proxy Cache and choose private-ecr from the pull-down list. Save the configuration by clicking on OK.
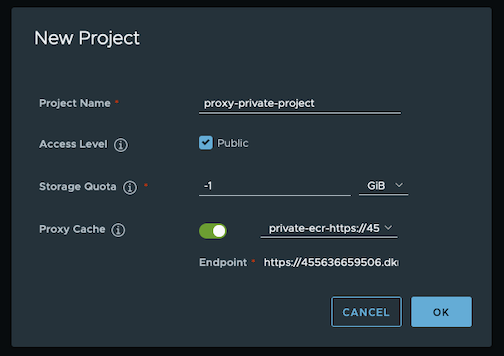
-
Pull images
Create a repository in the target private ECR registry
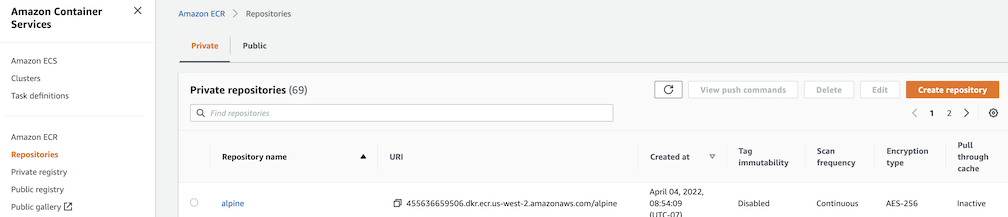
Push an image to the created repository
docker pull alpine
docker tag alpine [ACCOUNT NUMBER].dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/alpine:latest
docker push [ACCOUNT NUMBER].dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/alpine:latest
Note
harbor.eksa.demo:30003 should be replaced with whatever externalURL is set to in the Harbor package YAML file.
docker pull harbor.eksa.demo:30003/proxy-private-project/alpine:latest
Repository replication from Harbor to a private Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) repository
This use case is to use Harbor to replicate local images and charts to a private ECR repository in push mode. When a replication rule is set, all resources that match the defined filter patterns are replicated to the destination registry when the triggering condition is met.
-
Login
Log in to the Harbor web portal with the default credential as shown below

-
Create a nonproxy project
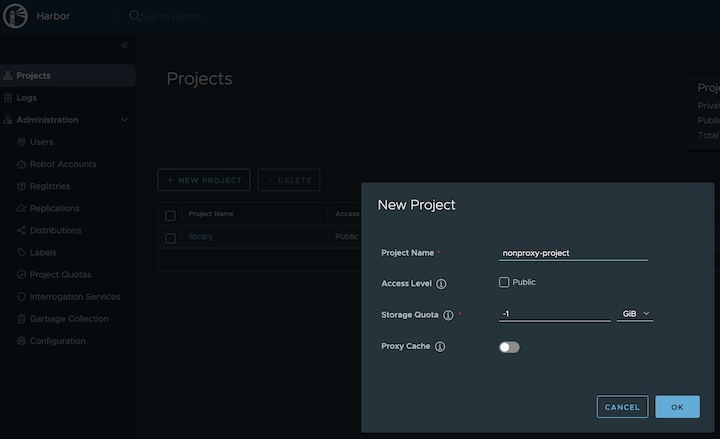
-
Create a registry proxy
In order for Harbor to proxy a remote private ECR registry, an IAM credential with necessary permissions need to be created. Usually, it follows three steps:
-
Policy
This is where you specify all necessary permissions. Please refer to private repository policies
, IAM permissions for pushing an image
and ECR policy examples
to figure out the minimal set of required permissions.
For simplicity, the build-in policy AdministratorAccess is used here.

-
User group
This is an easy way to manage a pool of users who share the same set of permissions by attaching the policy to the group.

-
User
Create a user and add it to the user group. In addition, please navigate to Security credentials to generate an access key. Access keys consists of two parts: an access key ID and a secret access key. Please save both as they are used in the next step.

Navigate to Registries on the left panel, and then click on the NEW ENDPOINT button. Choose Aws ECR as the Provider, and enter private-ecr as the Name, https://[ACCOUNT NUMBER].dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/ as the Endpoint URL, use the access key ID part of the generated access key as Access ID, and use the secret access key part of the generated access key as Access Secret. Save it by clicking on OK.

-
Create a replication rule
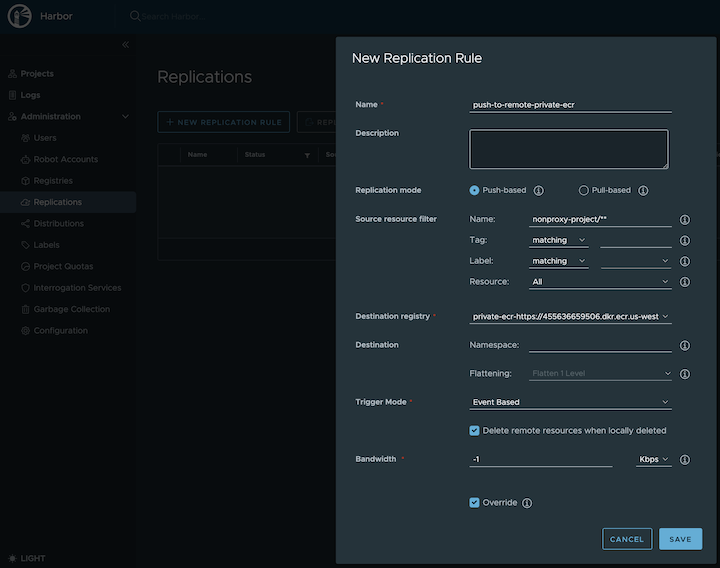
-
Prepare an image
Note
harbor.eksa.demo:30003 should be replaced with whatever externalURL is set to in the Harbor package YAML file.
docker pull alpine
docker tag alpine:latest harbor.eksa.demo:30003/nonproxy-project/alpine:latest
-
Authenticate with Harbor with the default credential as shown below
Note
harbor.eksa.demo:30003 should be replaced with whatever externalURL is set to in the Harbor package YAML file.
docker logout
docker login harbor.eksa.demo:30003
-
Push images
Create a repository in the target private ECR registry

Note
harbor.eksa.demo:30003 should be replaced with whatever externalURL is set to in the Harbor package YAML file.
docker push harbor.eksa.demo:30003/nonproxy-project/alpine:latest
The image should appear in the target ECR repository shortly.
Set up trivy image scanner in an air-gapped environment
This use case is to manually import vulnerability database to Harbor trivy when Harbor is running in an air-gapped environment. All the following commands are assuming Harbor is running in the default namespace.
-
Configure trivy
TLS example with auto certificate generation
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-harbor
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packageName: harbor
config: |-
secretKey: "use-a-secret-key"
externalURL: https://harbor.eksa.demo:30003
expose:
tls:
certSource: auto
auto:
commonName: "harbor.eksa.demo"
trivy:
skipUpdate: true
offlineScan: true
Non-TLS example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: my-harbor
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packageName: harbor
config: |-
secretKey: "use-a-secret-key"
externalURL: http://harbor.eksa.demo:30002
expose:
tls:
enabled: false
trivy:
skipUpdate: true
offlineScan: true
If Harbor is already running without the above trivy configurations, run the following command to update both skipUpdate and offlineScan
kubectl edit statefulsets/harbor-helm-trivy
-
Download the vulnerability database to your local host
Please follow oras installation instruction
.
oras pull ghcr.io/aquasecurity/trivy-db:2 -a
-
Upload database to trivy pod from your local host
kubectl cp db.tar.gz harbor-helm-trivy-0:/home/scanner/.cache/trivy -c trivy
-
Set up database on Harbor trivy pod
kubectl exec -it harbor-helm-trivy-0 -c trivy bash
cd /home/scanner/.cache/trivy
mkdir db
mv db.tar.gz db
cd db
tar zxvf db.tar.gz
15.3 - v2.5.0
Trivy, Notary and Chartmuseum are not supported at this moment.
Configuring Harbor in EKS Anywhere package spec
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the Harbor package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
externalURL |
The external URL for Harbor core service |
https://127.0.0.1:30003 |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
logLevel |
The log level: debug, info, warning, error or fatal |
info |
harborAdminPassword |
The initial password of the Harbor admin account. Change it from the portal after launching Harbor |
Harbor12345 |
secretKey |
The key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars |
"" |
| Expose |
|
|
expose.type |
How to expose the service: nodePort or loadBalancer, other values will be ignored and the creation of the service will be skipped. |
nodePort |
expose.tls.enabled |
Enable TLS or not. |
true |
expose.tls.certSource |
The source of the TLS certificate. Set as auto, secret or none and fill the information in the corresponding section: 1) auto: generate the TLS certificate automatically 2) secret: read the TLS certificate from the specified secret. The TLS certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager 3) none: configure no TLS certificate. |
secret |
expose.tls.auto.commonName |
The common name used to generate the certificate. It’s necessary when expose.tls.certSource is set to auto |
|
expose.tls.secret.secretName |
The name of the secret which contains keys named: tls.crt - the certificate; tls.key - the private key |
harbor-tls-secret |
expose.nodePort.name |
The name of the NodePort service |
harbor |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
30002 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
443 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30003 |
expose.loadBalancer.name |
The name of the service |
harbor |
expose.loadBalancer.IP |
The IP address of the loadBalancer. It only works when the loadBalancer supports assigning an IP address |
"" |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpsPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30002 |
expose.loadBalancer.annotations |
The annotations attached to the loadBalancer service |
{} |
expose.loadBalancer.sourceRanges |
List of IP address ranges to assign to loadBalancerSourceRanges |
[] |
| Internal TLS |
|
|
internalTLS.enabled |
Enable TLS for the components (core, jobservice, portal, and registry) |
true |
| Persistence |
|
|
persistence.resourcePolicy |
Setting it to keep to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart is deleted. Does not affect PVCs created for internal database and redis components. |
keep |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.size |
The size of the volume |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.size |
The size of the volume. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.size |
The size of the volume. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volumem, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
| Registry |
|
|
registry.relativeurls |
If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. Needed if harbor is behind a reverse proxy |
false |
15.4 - v2.5.1
Notary and Chartmuseum are not supported at this moment.
Configuring Harbor in EKS Anywhere package spec
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the Harbor package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
externalURL |
The external URL for Harbor core service |
https://127.0.0.1:30003 |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
logLevel |
The log level: debug, info, warning, error or fatal |
info |
harborAdminPassword |
The initial password of the Harbor admin account. Change it from the portal after launching Harbor |
Harbor12345 |
secretKey |
The key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars |
"" |
| Expose |
|
|
expose.type |
How to expose the service: nodePort or loadBalancer, other values will be ignored and the creation of the service will be skipped. |
nodePort |
expose.tls.enabled |
Enable TLS or not. |
true |
expose.tls.certSource |
The source of the TLS certificate. Set as auto, secret or none and fill the information in the corresponding section: 1) auto: generate the TLS certificate automatically 2) secret: read the TLS certificate from the specified secret. The TLS certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager 3) none: configure no TLS certificate. |
secret |
expose.tls.auto.commonName |
The common name used to generate the certificate. It’s necessary when expose.tls.certSource is set to auto |
|
expose.tls.secret.secretName |
The name of the secret which contains keys named: tls.crt - the certificate; tls.key - the private key |
harbor-tls-secret |
expose.nodePort.name |
The name of the NodePort service |
harbor |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
30002 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
443 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30003 |
expose.loadBalancer.name |
The name of the service |
harbor |
expose.loadBalancer.IP |
The IP address of the loadBalancer. It only works when loadBalancer supports assigning an IP address |
"" |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpsPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30002 |
expose.loadBalancer.annotations |
The annotations attached to the loadBalancer service |
{} |
expose.loadBalancer.sourceRanges |
List of IP address ranges to assign to loadBalancerSourceRanges |
[] |
| Internal TLS |
|
|
internalTLS.enabled |
Enable TLS for the components (core, jobservice, portal, and registry) |
true |
| Persistence |
|
|
persistence.resourcePolicy |
Setting it to keep to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart is deleted. Does not affect PVCs created for internal database and redis components. |
keep |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.size |
The size of the volume |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.size |
The size of the volume. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.size |
The size of the volume. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
| Trivy |
|
|
trivy.enabled |
The flag to enable Trivy scanner |
true |
trivy.vulnType |
Comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values os and library. |
os,library |
trivy.severity |
Comma-separated list of severities to be checked |
UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL |
trivy.skipUpdate |
The flag to disable Trivy DB
downloads from GitHub |
false |
trivy.offlineScan |
The flag prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. |
false |
| Registry |
|
|
registry.relativeurls |
If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. Needed if harbor is behind a reverse proxy |
false |
15.5 - v2.10.2
Configuring Harbor in EKS Anywhere package spec
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the Harbor package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
externalURL |
The external URL for Harbor core service |
https://127.0.0.1:30003 |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
logLevel |
The log level: debug, info, warning, error or fatal |
info |
harborAdminPassword |
The initial password of the Harbor admin account. Change it from the portal after launching Harbor |
Harbor12345 |
secretKey |
The key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars |
"" |
| Expose |
|
|
expose.type |
How to expose the service: nodePort or loadBalancer, other values will be ignored and the creation of the service will be skipped. |
nodePort |
expose.tls.enabled |
Enable TLS or not. |
true |
expose.tls.certSource |
The source of the TLS certificate. Set as auto, secret or none and fill the information in the corresponding section: 1) auto: generate the TLS certificate automatically 2) secret: read the TLS certificate from the specified secret. The TLS certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager 3) none: configure no TLS certificate. |
secret |
expose.tls.auto.commonName |
The common name used to generate the certificate. It’s necessary when expose.tls.certSource is set to auto |
|
expose.tls.secret.secretName |
The name of the secret which contains keys named: tls.crt - the certificate; tls.key - the private key |
harbor-tls-secret |
expose.nodePort.name |
The name of the NodePort service |
harbor |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
30002 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
443 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30003 |
expose.loadBalancer.name |
The name of the service |
harbor |
expose.loadBalancer.IP |
The IP address of the loadBalancer. It only works when loadBalancer supports assigning an IP address |
"" |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpsPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30002 |
expose.loadBalancer.annotations |
The annotations attached to the loadBalancer service |
{} |
expose.loadBalancer.sourceRanges |
List of IP address ranges to assign to loadBalancerSourceRanges |
[] |
| Internal TLS |
|
|
internalTLS.enabled |
Enable TLS for the components (core, jobservice, portal, and registry) |
true |
| Persistence |
|
|
persistence.resourcePolicy |
Setting it to keep to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart is deleted. Does not affect PVCs created for internal database and redis components. |
keep |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.jobLog.size |
The size of the volume |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.jobLog.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.size |
The size of the volume. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.size |
The size of the volume. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
| Trivy |
|
|
trivy.enabled |
The flag to enable Trivy scanner |
true |
trivy.vulnType |
Comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values os and library. |
os,library |
trivy.severity |
Comma-separated list of severities to be checked |
UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL |
trivy.skipUpdate |
The flag to disable Trivy DB
downloads from GitHub |
false |
trivy.offlineScan |
The flag prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. |
false |
| Registry |
|
|
registry.relativeurls |
If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. Needed if harbor is behind a reverse proxy |
false |
15.6 - v2.7.1
Notary and Chartmuseum are not supported at this moment.
Configuring Harbor in EKS Anywhere package spec
The following table lists the configurable parameters of the Harbor package spec and the default values.
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
externalURL |
The external URL for Harbor core service |
https://127.0.0.1:30003 |
imagePullPolicy |
The image pull policy |
IfNotPresent |
logLevel |
The log level: debug, info, warning, error or fatal |
info |
harborAdminPassword |
The initial password of the Harbor admin account. Change it from the portal after launching Harbor |
Harbor12345 |
secretKey |
The key used for encryption. Must be a string of 16 chars |
"" |
| Expose |
|
|
expose.type |
How to expose the service: nodePort or loadBalancer, other values will be ignored and the creation of the service will be skipped. |
nodePort |
expose.tls.enabled |
Enable TLS or not. |
true |
expose.tls.certSource |
The source of the TLS certificate. Set as auto, secret or none and fill the information in the corresponding section: 1) auto: generate the TLS certificate automatically 2) secret: read the TLS certificate from the specified secret. The TLS certificate can be generated manually or by cert manager 3) none: configure no TLS certificate. |
secret |
expose.tls.auto.commonName |
The common name used to generate the certificate. It’s necessary when expose.tls.certSource is set to auto |
|
expose.tls.secret.secretName |
The name of the secret which contains keys named: tls.crt - the certificate; tls.key - the private key |
harbor-tls-secret |
expose.nodePort.name |
The name of the NodePort service |
harbor |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.nodePort.ports.http.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
30002 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.port |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
443 |
expose.nodePort.ports.https.nodePort |
The node port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30003 |
expose.loadBalancer.name |
The name of the service |
harbor |
expose.loadBalancer.IP |
The IP address of the loadBalancer. It only works when loadBalancer supports assigning an IP address |
"" |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTP |
80 |
expose.loadBalancer.ports.httpsPort |
The service port Harbor listens on when serving HTTPS |
30002 |
expose.loadBalancer.annotations |
The annotations attached to the loadBalancer service |
{} |
expose.loadBalancer.sourceRanges |
List of IP address ranges to assign to loadBalancerSourceRanges |
[] |
| Internal TLS |
|
|
internalTLS.enabled |
Enable TLS for the components (core, jobservice, portal, and registry) |
true |
| Persistence |
|
|
persistence.resourcePolicy |
Setting it to keep to avoid removing PVCs during a helm delete operation. Leaving it empty will delete PVCs after the chart is deleted. Does not affect PVCs created for internal database and redis components. |
keep |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.registry.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.jobLog.size |
The size of the volume |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.jobservice.jobLog.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.size |
The size of the volume. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.database.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external database is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.size |
The size of the volume. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
1Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.redis.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning. If an external Redis is used, the setting will be ignored |
"" |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.size |
The size of the volume |
5Gi |
persistence.persistentVolumeClaim.trivy.storageClass |
Specify the storageClass used to provision the volume, or the default StorageClass will be used (the default). Set it to - to disable dynamic provisioning |
"" |
| Trivy |
|
|
trivy.enabled |
The flag to enable Trivy scanner |
true |
trivy.vulnType |
Comma-separated list of vulnerability types. Possible values os and library. |
os,library |
trivy.severity |
Comma-separated list of severities to be checked |
UNKNOWN,LOW,MEDIUM,HIGH,CRITICAL |
trivy.skipUpdate |
The flag to disable Trivy DB
downloads from GitHub |
false |
trivy.offlineScan |
The flag prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. |
false |
| Registry |
|
|
registry.relativeurls |
If true, the registry returns relative URLs in Location headers. The client is responsible for resolving the correct URL. Needed if harbor is behind a reverse proxy |
false |
16 - MetalLB Configuration
MetalLB is a load-balancer implementation for on-premises Kubernetes clusters, using standard routing protocols.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
16.1 - MetalLB
Install/upgrade/uninstall MetalLB
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package metallb --cluster <cluster-name> > metallb.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to metallb.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file with bgp configuration:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metallb
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.120
BGPAdvertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
BGPPeers:
- peerAddress: 10.220.0.2
peerASN: 65000
myASN: 65002
Example package file with ARP configuration:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages
spec:
packageName: metallb
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.120
L2Advertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
-
Create the namespace
(If overriding targetNamespace, change metallb-system to the value of targetNamespace)
kubectl create namespace metallb-system
-
Install MetalLB
eksctl anywhere create packages -f metallb.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
mylb metallb 22h installed 0.13.5-ce5b5de19014202cebd4ab4c091830a3b6dfea06 0.13.5-ce5b5de19014202cebd4ab4c091830a3b6dfea06 (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update metallb.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f metallb.yaml
Upgrade
MetalLB will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall MetalLB, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> mylb
16.2 - v0.12.1
FRRouting
is currently not supported for MetalLB.
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metallb
targetNamespace: metallb-system
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.94/32
- 10.220.0.95/32
- name: bgp
addresses:
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.99
L2Advertisements:
- IPAddressPools:
- default
BGPAdvertisements:
- IPAddressPools:
- bgp
BGPPeers:
- myASN: 123
peerASN: 55001
peerAddress: 1.2.3.4
keepaliveTime: 30s
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| IPAddressPools[] |
A list of IPAddressPool. |
None |
| L2Advertisements[] |
A list of L2Advertisement. |
None |
| BGPAdvertisements[] |
A list of BGPAdvertisement. |
None |
| BGPPeers[] |
A list of BGPPeer. |
None |
| — |
— |
— |
| IPAddressPool |
A list of IP address ranges over which MetalLB has authority. You can list multiple ranges in a single pool and they will all share the same settings. Each range can be either a CIDR prefix, or an explicit start-end range of IPs. |
|
| name |
Name for the address pool. |
None |
| addresses[] |
A list of string representing CIRD or IP ranges. |
None |
| autoAssign |
AutoAssign flag used to prevent MetalLB from automatic allocation for a pool. |
true |
| — |
— |
— |
| L2Advertisement |
L2Advertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the LoadBalancer IPs provided by the selected pools via L2. |
|
| IPAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPools to advertise via this advertisement, selected by name. |
None |
| — |
— |
— |
| BGPAdvertisement |
BGPAdvertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the IPs coming from the selected IPAddressPools via BGP, setting the parameters of the BGP Advertisement. |
|
| aggregationLength |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /32s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 32. Works for IPv4 addresses. |
32 |
| aggregationLengthV6 |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /128s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 128. Works for IPv6 addresses. |
128 |
| communities[] |
The BGP communities to be associated with the announcement. Each item can be a community of the form 1234:1234 or the name of an alias defined in the Community CRD. |
None |
| IPAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPools to advertise via this advertisement, selected by name. |
None |
| localPref |
The BGP LOCAL_PREF attribute which is used by BGP best path algorithm, Path with higher localpref is preferred over one with lower localpref. |
None |
| — |
— |
— |
| BGPPeer |
Peers for the BGP protocol. |
|
| bfdProfile |
The name of the BFD Profile to be used for the BFD session associated to the BGP session. If not set, the BFD session won’t be set up. |
None |
| holdTime |
Requested BGP hold time, per RFC4271. |
None |
| keepaliveTime |
Requested BGP keepalive time, per RFC4271. |
None |
| myASN |
AS number to use for the local end of the session. |
None |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
| peerASN |
AS number to expect from the remote end of the session. |
None |
| peerAddress |
Address to dial when establishing the session. |
None |
| peerPort |
Port to dial when establishing the session. |
179 |
| routerID |
BGP router ID to advertise to the peer. |
None |
| sourceAddress |
Source address to use when establishing the session. |
None |
16.3 - v0.13.5
FRRouting
is currently not supported for MetalLB.
Starting at v0.13.5, keys within each config section start with lowercase. For example:
L2Advertisements:
- IPAddressPools:
- default
Becomes:
L2Advertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
Top-level section names remain capitalized as they represent CRDs:
config: |
IPAddressPools:
...
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metallb
targetNamespace: metallb-system
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.94/32
- 10.220.0.95/32
- name: bgp
addresses:
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.99
L2Advertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
BGPAdvertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- bgp
autoAssign: false
BGPPeers:
- myASN: 123
peerASN: 55001
peerAddress: 1.2.3.4
keepaliveTime: 30s
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Required |
| IPAddressPools[] |
A list of ip address pools. See IPAddressPool. |
None |
False |
| L2Advertisements[] |
A list of Layer 2 advertisements. See L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPAdvertisements[] |
A list of BGP advertisements. See BGPAdvertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPPeers[] |
A list of BGP peers. See BGPPeer. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| IPAddressPool |
A list of IP address ranges over which MetalLB has authority. You can list multiple ranges in a single pool and they will all share the same settings. Each range can be either a CIDR prefix, or an explicit start-end range of IPs. |
|
|
| name |
Name for the address pool. |
None |
True |
| addresses[] |
A list of string representing CIRD or IP ranges. |
None |
True |
| autoAssign |
AutoAssign flag used to prevent MetalLB from automatic allocation for a pool. |
true |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| L2Advertisement |
L2Advertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the LoadBalancer IPs provided by the selected pools via L2. |
|
|
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to advertise. |
None |
True |
| name |
Name for the L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPAdvertisement |
BGPAdvertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the IPs coming from the selected ipAddressPools via BGP, setting the parameters of the BGP Advertisement. |
|
|
| aggregationLength |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /32s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 32. Works for IPv4 addresses. |
32 |
False |
| aggregationLengthV6 |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /128s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 128. Works for IPv6 addresses. |
128 |
False |
| communities[] |
The BGP communities to be associated with the announcement. Each item can be a community of the form 1234:1234 or the name of an alias defined in the Community CRD. |
None |
False |
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to be advertised via BGP. |
None |
True |
| localPref |
The BGP LOCAL_PREF attribute which is used by BGP best path algorithm, Path with higher localpref is preferred over one with lower localpref. |
None |
False |
| peers[] |
List of peer names. Limits the bgppeer to advertise the ips of the selected pools to. When empty, the loadbalancer IP is announced to all the BGPPeers configured. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPPeer |
Peers for the BGP protocol. |
|
|
| holdTime |
Requested BGP hold time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| keepaliveTime |
Requested BGP keepalive time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| myASN |
AS number to use for the local end of the session. |
None |
True |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
False |
| peerASN |
AS number to expect from the remote end of the session. |
None |
True |
| peerAddress |
Address to dial when establishing the session. |
None |
True |
| peerPort |
Port to dial when establishing the session. |
179 |
False |
| routerID |
BGP router ID to advertise to the peer. |
None |
False |
| sourceAddress |
Source address to use when establishing the session. |
None |
False |
16.4 - v0.13.7
FRRouting
is currently not supported for MetalLB.
Starting at v0.13.5, keys within each config section start with lowercase.
See v0.13.5
for details.
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metallb
targetNamespace: metallb-system
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.94/32
- 10.220.0.95/32
- name: bgp
addresses:
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.99
L2Advertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
BGPAdvertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- bgp
autoAssign: false
BGPPeers:
- myASN: 123
peerASN: 55001
peerAddress: 1.2.3.4
keepaliveTime: 30s
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Required |
| IPAddressPools[] |
A list of ip address pools. See IPAddressPool. |
None |
False |
| L2Advertisements[] |
A list of Layer 2 advertisements. See L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPAdvertisements[] |
A list of BGP advertisements. See BGPAdvertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPPeers[] |
A list of BGP peers. See BGPPeer. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| IPAddressPool |
A list of IP address ranges over which MetalLB has authority. You can list multiple ranges in a single pool and they will all share the same settings. Each range can be either a CIDR prefix, or an explicit start-end range of IPs. |
|
|
| name |
Name for the address pool. |
None |
True |
| addresses[] |
A list of string representing CIRD or IP ranges. |
None |
True |
| autoAssign |
AutoAssign flag used to prevent MetalLB from automatic allocation for a pool. |
true |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| L2Advertisement |
L2Advertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the LoadBalancer IPs provided by the selected pools via L2. |
|
|
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to advertise. |
None |
True |
| name |
Name for the L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPAdvertisement |
BGPAdvertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the IPs coming from the selected ipAddressPools via BGP, setting the parameters of the BGP Advertisement. |
|
|
| aggregationLength |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /32s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 32. Works for IPv4 addresses. |
32 |
False |
| aggregationLengthV6 |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /128s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 128. Works for IPv6 addresses. |
128 |
False |
| communities[] |
The BGP communities to be associated with the announcement. Each item can be a community of the form 1234:1234 or the name of an alias defined in the Community CRD. |
None |
False |
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to be advertised via BGP. |
None |
True |
| localPref |
The BGP LOCAL_PREF attribute which is used by BGP best path algorithm, Path with higher localpref is preferred over one with lower localpref. |
None |
False |
| peers[] |
List of peer names. Limits the bgppeer to advertise the ips of the selected pools to. When empty, the loadbalancer IP is announced to all the BGPPeers configured. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPPeer |
Peers for the BGP protocol. |
|
|
| holdTime |
Requested BGP hold time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| keepaliveTime |
Requested BGP keepalive time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| myASN |
AS number to use for the local end of the session. |
None |
True |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
False |
| peerASN |
AS number to expect from the remote end of the session. |
None |
True |
| peerAddress |
Address to dial when establishing the session. |
None |
True |
| peerPort |
Port to dial when establishing the session. |
179 |
False |
| routerID |
BGP router ID to advertise to the peer. |
None |
False |
| sourceAddress |
Source address to use when establishing the session. |
None |
False |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
False |
| passwordSecret |
passwordSecret is a reference to the authentication secret for BGP Peer. The secret must be of type ‘kubernetes.io/basic-auth’ and the password stored under the “password” key. Example:
passwordSecret:
name: mySecret
namespace: metallb-system |
None |
False |
16.5 - v0.14.5
FRRouting
is currently not supported for MetalLB.
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: mylb
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metallb
targetNamespace: metallb-system
config: |
IPAddressPools:
- name: default
addresses:
- 10.220.0.93/32
- 10.220.0.94/32
- 10.220.0.95/32
- name: bgp
addresses:
- 10.220.0.97-10.220.0.99
L2Advertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- default
BGPAdvertisements:
- ipAddressPools:
- bgp
autoAssign: false
BGPPeers:
- myASN: 123
peerASN: 55001
peerAddress: 1.2.3.4
keepaliveTime: 30s
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
Required |
| IPAddressPools[] |
A list of ip address pools. See IPAddressPool. |
None |
False |
| L2Advertisements[] |
A list of Layer 2 advertisements. See L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPAdvertisements[] |
A list of BGP advertisements. See BGPAdvertisement. |
None |
False |
| BGPPeers[] |
A list of BGP peers. See BGPPeer. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| IPAddressPool |
A list of IP address ranges over which MetalLB has authority. You can list multiple ranges in a single pool and they will all share the same settings. Each range can be either a CIDR prefix, or an explicit start-end range of IPs. |
|
|
| name |
Name for the address pool. |
None |
True |
| addresses[] |
A list of string representing CIRD or IP ranges. |
None |
True |
| autoAssign |
AutoAssign flag used to prevent MetalLB from automatic allocation for a pool. |
true |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| L2Advertisement |
L2Advertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the LoadBalancer IPs provided by the selected pools via L2. |
|
|
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to advertise. |
None |
True |
| name |
Name for the L2Advertisement. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPAdvertisement |
BGPAdvertisement allows MetalLB to advertise the IPs coming from the selected ipAddressPools via BGP, setting the parameters of the BGP Advertisement. |
|
|
| aggregationLength |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /32s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 32. Works for IPv4 addresses. |
32 |
False |
| aggregationLengthV6 |
The aggregation-length advertisement option lets you “roll up” the /128s into a larger prefix. Defaults to 128. Works for IPv6 addresses. |
128 |
False |
| communities[] |
The BGP communities to be associated with the announcement. Each item can be a community of the form 1234:1234 or the name of an alias defined in the Community CRD. |
None |
False |
| ipAddressPools[] |
The list of IPAddressPool names to be advertised via BGP. |
None |
True |
| localPref |
The BGP LOCAL_PREF attribute which is used by BGP best path algorithm, Path with higher localpref is preferred over one with lower localpref. |
None |
False |
| peers[] |
List of peer names. Limits the bgppeer to advertise the ips of the selected pools to. When empty, the loadbalancer IP is announced to all the BGPPeers configured. |
None |
False |
| — |
— |
— |
— |
| BGPPeer |
Peers for the BGP protocol. |
|
|
| holdTime |
Requested BGP hold time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| keepaliveTime |
Requested BGP keepalive time, per RFC4271. |
None |
False |
| myASN |
AS number to use for the local end of the session. |
None |
True |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
False |
| peerASN |
AS number to expect from the remote end of the session. |
None |
True |
| peerAddress |
Address to dial when establishing the session. |
None |
True |
| peerPort |
Port to dial when establishing the session. |
179 |
False |
| routerID |
BGP router ID to advertise to the peer. |
None |
False |
| sourceAddress |
Source address to use when establishing the session. |
None |
False |
| password |
Authentication password for routers enforcing TCP MD5 authenticated sessions. |
None |
False |
| passwordSecret |
passwordSecret is a reference to the authentication secret for BGP Peer. The secret must be of type ‘kubernetes.io/basic-auth’ and the password stored under the “password” key. Example:
passwordSecret:
name: mySecret
namespace: metallb-system |
None |
False |
17 - Prometheus Configuration
Prometheus is an open-source systems monitoring and alerting toolkit. It collects and stores metrics as time series data.
Best Practice
Any supported EKS Anywhere curated package should be modified through package yaml files (with kind: Package) and applied through the command eksctl anywhere apply package -f packageFileName. Modifying objects outside of package yaml files may lead to unpredictable behaviors.
For automatic namespace (targetNamespace) creation, see createNamespace field: PackagebundleController.spec
Configuration options for Prometheus
17.1 - Prometheus with Grafana
This tutorial demonstrates how to config the Prometheus package to scrape metrics from an EKS Anywhere cluster, and visualize them in Grafana.
This tutorial walks through the following procedures:
Install the Prometheus package
The Prometheus package creates two components by default:
- Prometheus-server,
which collects metrics from configured targets, and stores the metrics as time series data;
- Node-exporter,
which exposes a wide variety of hardware- and kernel-related metrics for prometheus-server (or an equivalent metrics collector, i.e. ADOT collector) to scrape.
The prometheus-server is pre-configured to scrape the following targets at 1m interval:
- Kubernetes API servers
- Kubernetes nodes
- Kubernetes nodes cadvisor
- Kubernetes service endpoints
- Kubernetes services
- Kubernetes pods
- Prometheus-server itself
If no config modification is needed, a user can proceed to the Prometheus installation guide
.
Prometheus Package Customization
In this section, we cover a few frequently-asked config customizations. After determining the appropriate customization, proceed to the Prometheus installation guide
to complete the package installation. Also refer to Prometheus package spec
for additional config options.
Change prometheus-server global configs
By default, prometheus-server is configured with evaluation_interval: 1m, scrape_interval: 1m, scrape_timeout: 10s. Those values can be overwritten if preferred / needed.
The following config allows the user to do such customization:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
config: |
server:
global:
evaluation_interval: "30s"
scrape_interval: "30s"
scrape_timeout: "15s"
Run prometheus-server as statefulSets
By default, prometheus-server is created as a deployment with replicaCount equals to 1. If there is a need to increase the replicaCount greater than 1, a user should deploy prometheus-server as a statefulSet instead. This allows multiple prometheus-server pods to share the same data storage.
The following config allows the user to do such customization:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
config: |
server:
replicaCount: 2
statefulSet:
enabled: true
Disable prometheus-server and use node-exporter only
A user may disable the prometheus-server when:
- they would like to use node-exporter to expose hardware- and kernel-related metrics, while
- they have deployed another metrics collector in the cluster and configured a remote-write storage solution, which fulfills the prometheus-server functionality (check out the ADOT with Amazon Managed Prometheus and Amazon Managed Grafana workshop
to learn how to do so).
The following config allows the user to do such customization:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
config: |
server:
enabled: false
Disable node-exporter and use prometheus-server only
A user may disable the node-exporter when:
- they would like to deploy multiple prometheus-server packages for a cluster, while
- deploying only one or none node-exporter instance per node.
The following config allows the user to do such customization:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
config: |
nodeExporter:
enabled: false
Prometheus Package Test
To ensure the Prometheus package is installed correctly in the cluster, a user can perform the following tests.
Access prometheus-server web UI
Port forward Prometheus to local host 9090:
export PROM_SERVER_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace <namespace> -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=prometheus,app.kubernetes.io/component=server" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name")
kubectl port-forward $PROM_SERVER_POD_NAME -n <namespace> 9090
Go to http://localhost:9090
to access the web UI.
Run sample queries
Run sample queries in Prometheus web UI to confirm the targets have been configured properly. For example, a user can run the following query to obtain the CPU utilization rate by node.
100 - (avg by(instance) (irate(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="idle"}[5m])) * 100 )
The output will be displayed on the Graph tab.
Install Grafana helm charts
A user can install Grafana in the cluster to visualize the Prometheus metrics. We used the Grafana helm chart as an example below, though other deployment methods are also possible.
-
Get helm chart repo info
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
-
Install the helm chart
helm install my-grafana grafana/grafana
Set up Grafana dashboards
Access Grafana web UI
-
Obtain Grafana login password:
kubectl get secret --namespace default my-grafana -o jsonpath="{.data.admin-password}" | base64 --decode; echo
-
Port forward Grafana to local host 3000:
export GRAFANA_POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace default -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=grafana,app.kubernetes.io/instance=my-grafana" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
kubectl --namespace default port-forward $GRAFANA_POD_NAME 3000
-
Go to http://localhost:3000
to access the web UI.
Log in with username admin, and password obtained from the Obtain Grafana login password in step 1 above.
Add Prometheus data source
-
Click on the Configuration sign on the left navigation bar, select Data sources, then choose Prometheus as the Data source.
-
Configure Prometheus data source with the following details:
- Name:
Prometheus as an example.
- URL:
http://<prometheus-server-end-point-name>.<namespace>:9090. If the package default values are used, this will be http://generated-prometheus-server.observability:9090.
- Scrape interval:
1m or the value specified by user in the package config.
- Select
Save and test. A notification data source is working should be displayed.
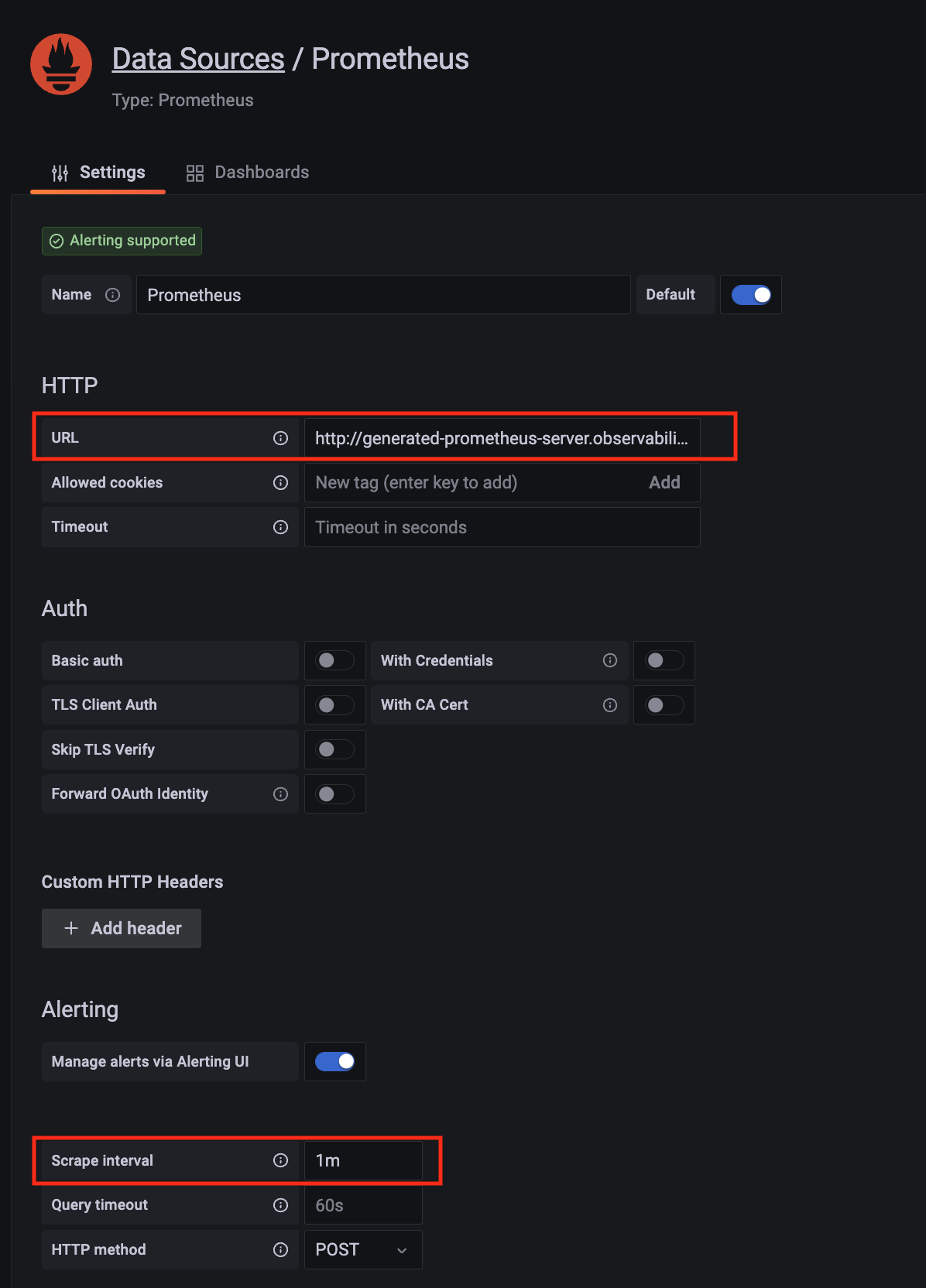
Import dashboard templates
-
Import a dashboard template by hovering over to the Dashboard sign on the left navigation bar, and click on Import. Type 315 in the Import via grafana.com textbox and select Import.
From the dropdown at the bottom, select Prometheus and select Import.
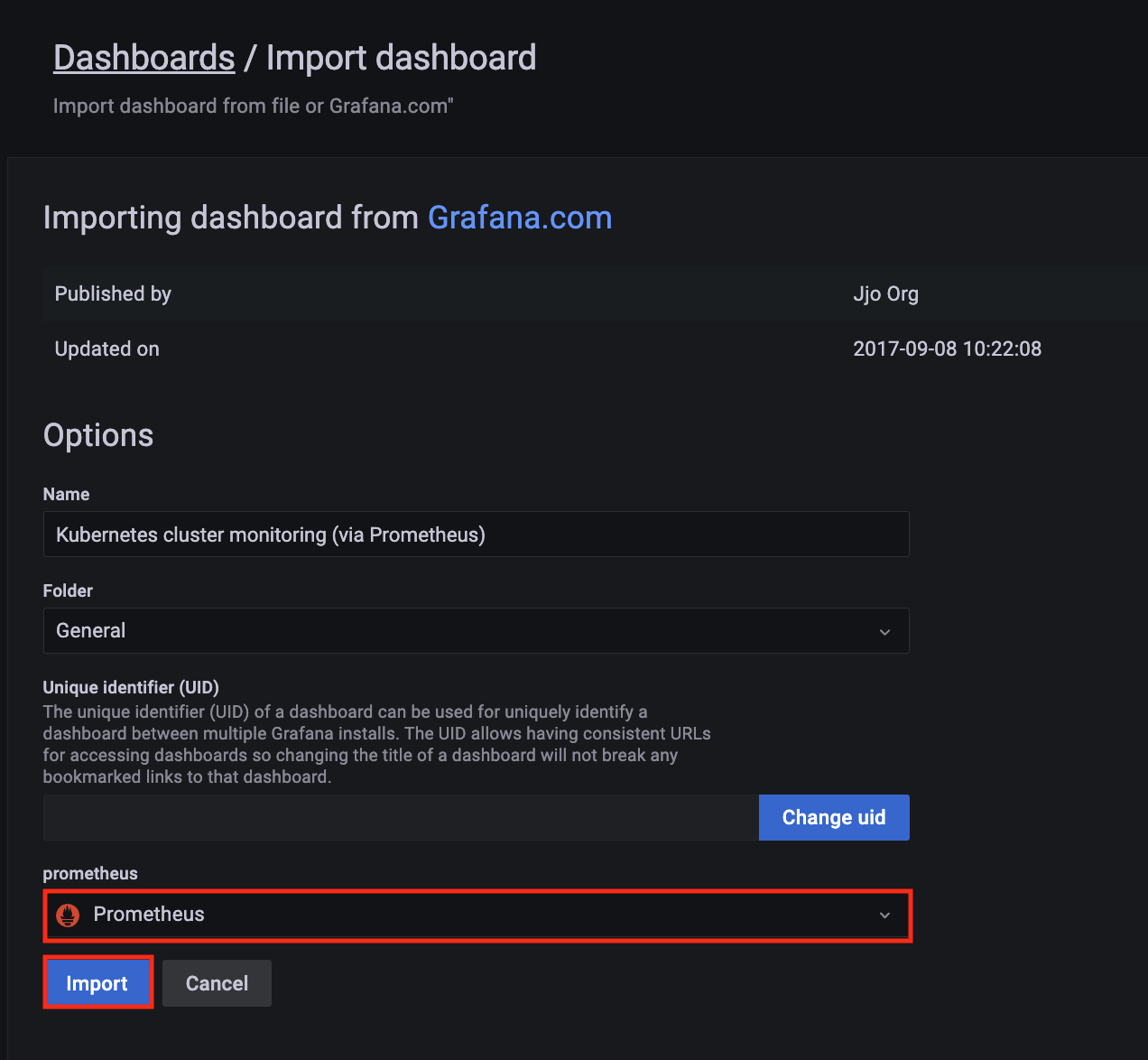
-
A Kubernetes cluster monitoring (via Prometheus) dashboard will be displayed.
-
Perform the same procedure for template 1860. A Node Exporter Full dashboard will be displayed.
17.2 - Prometheus
Install/upgrade/uninstall Prometheus
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package prometheus --cluster <cluster-name> > prometheus.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to prometheus.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file with default configuration, which enables prometheus-server and node-exporter:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
Example package file with prometheus-server (or node-exporter) disabled:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
config: |
# disable prometheus-server
server:
enabled: false
# or disable node-exporter
# nodeExporter:
# enabled: false
Example package file with prometheus-server deployed as a statefulSet with replicaCount 2, and set scrape config to collect Prometheus-server’s own metrics only:
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
server:
replicaCount: 2
statefulSet:
enabled: true
serverFiles:
prometheus.yml:
scrape_configs:
- job_name: prometheus
static_configs:
- targets:
- localhost:9090
-
Create the namespace
(If overriding targetNamespace, change observability to the value of targetNamespace)
kubectl create namespace observability
-
Install prometheus
eksctl anywhere create packages -f prometheus.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAMESPACE NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
eksa-packages-<cluster-name> generated-prometheus prometheus 17m installed 2.41.0-b53c8be243a6cc3ac2553de24ab9f726d9b851ca 2.41.0-b53c8be243a6cc3ac2553de24ab9f726d9b851ca (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update prometheus.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f prometheus.yaml
Upgrade
Prometheus will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall Prometheus, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> generated-prometheus
17.3 - v2.39.1
Configuring Prometheus in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
server:
replicaCount: 2
statefulSet:
enabled: true
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| rbac.create |
Specifies if clusterRole / role and clusterRoleBinding / roleBinding will be created for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
true |
| sourceRegistry |
Specifies image source registry for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
"783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com" |
| Node-Exporter |
|
|
| nodeExporter.enabled |
Indicates if node-exporter is enabled |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostNetwork |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host network namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostPID |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host process ID namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies node-exporter image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| nodeExporter.image.repository |
Specifies node-exporter image repository |
"prometheus/node-exporter" |
| nodeExporter.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the node-exporter container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| nodeExporter.service |
Specifies how to expose node-exporter as a network service |
See footnote |
| nodeExporter.tolerations |
Specifies node tolerations for node-exporter scheduling to nodes with taints. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation toleration
field for more details. |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.annotations |
Specifies node-exporter service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.create |
Indicates if node-exporter service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.name |
Specifies node-exporter service account name |
"" |
| Prometheus-Server |
|
|
| server.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is enabled |
true |
| server.global.evaluation_interval |
Specifies how frequently the prometheus-server rules are evaluated |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_interval |
Specifies how frequently prometheus-server will scrape targets |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_timeout |
Specifies how long until a prometheus-server scrape request times out |
"10s" |
| server.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies prometheus-server image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| server.image.repository |
Specifies prometheus-server image repository |
"prometheus/prometheus" |
| server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server container name |
"server" |
| server.persistentVolume.accessModes |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume access modes |
"ReadWriteOnce" |
| server.persistentVolume.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim |
true |
| server.persistentVolume.existingClaim |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume existing claim name. It requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true. If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound |
"" |
| server.persistentVolume.size |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume size |
"8Gi" |
| server.remoteRead |
Specifies prometheus-server remote read configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_read
for more details |
[] |
| server.remoteWrite |
Specifies prometheus-server remote write configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_write
for more details |
[] |
| server.replicaCount |
Specifies the replicaCount for prometheus-server deployment / statefulSet. Note: server.statefulSet.enabled should be set to true if server.replicaCount is greater than 1 |
1 |
| server.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the prometheus-server container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| server.retention |
Specifies prometheus-server data retention period |
"15d" |
| server.service |
Specifies how to expose prometheus-server as a network service |
See footnote |
| server.statefulSet.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is deployed as a statefulSet. If set to false, prometheus-server will be deployed as a deployment |
false |
| serverFiles.“prometheus.yml”.scrape_configs |
Specifies a set of targets and parameters for prometheus-server describing how to scrape them. Refer to Prometheus docs scrape_config
for more details |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.server.annotations |
Specifies prometheus-server service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.server.create |
Indicates if prometheus-server service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server service account name |
"" |
17.4 - v2.41.1
Configuring Prometheus in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
server:
replicaCount: 2
statefulSet:
enabled: true
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| rbac.create |
Specifies if clusterRole / role and clusterRoleBinding / roleBinding will be created for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
true |
| sourceRegistry |
Specifies image source registry for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
"783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com" |
| Node-Exporter |
|
|
| nodeExporter.enabled |
Indicates if node-exporter is enabled |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostNetwork |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host network namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostPID |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host process ID namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies node-exporter image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| nodeExporter.image.repository |
Specifies node-exporter image repository |
"prometheus/node-exporter" |
| nodeExporter.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the node-exporter container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| nodeExporter.service |
Specifies how to expose node-exporter as a network service |
See footnote |
| nodeExporter.tolerations |
Specifies node tolerations for node-exporter scheduling to nodes with taints. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation toleration
field for more details. |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.annotations |
Specifies node-exporter service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.create |
Indicates if node-exporter service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.name |
Specifies node-exporter service account name |
"" |
| Prometheus-Server |
|
|
| server.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is enabled |
true |
| server.global.evaluation_interval |
Specifies how frequently the prometheus-server rules are evaluated |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_interval |
Specifies how frequently prometheus-server will scrape targets |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_timeout |
Specifies how long until a prometheus-server scrape request times out |
"10s" |
| server.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies prometheus-server image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| server.image.repository |
Specifies prometheus-server image repository |
"prometheus/prometheus" |
| server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server container name |
"server" |
| server.persistentVolume.accessModes |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume access modes |
"ReadWriteOnce" |
| server.persistentVolume.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim |
true |
| server.persistentVolume.existingClaim |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume existing claim name. It requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true. If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound |
"" |
| server.persistentVolume.size |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume size |
"8Gi" |
| server.remoteRead |
Specifies prometheus-server remote read configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_read
for more details |
[] |
| server.remoteWrite |
Specifies prometheus-server remote write configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_write
for more details |
[] |
| server.replicaCount |
Specifies the replicaCount for prometheus-server deployment / statefulSet. Note: server.statefulSet.enabled should be set to true if server.replicaCount is greater than 1 |
1 |
| server.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the prometheus-server container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| server.retention |
Specifies prometheus-server data retention period |
"15d" |
| server.service |
Specifies how to expose prometheus-server as a network service |
See footnote |
| server.statefulSet.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is deployed as a statefulSet. If set to false, prometheus-server will be deployed as a deployment |
false |
| serverFiles.“prometheus.yml”.scrape_configs |
Specifies a set of targets and parameters for prometheus-server describing how to scrape them. Refer to Prometheus docs scrape_config
for more details |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.server.annotations |
Specifies prometheus-server service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.server.create |
Indicates if prometheus-server service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server service account name |
"" |
17.5 - v2.52.0
Configuring Prometheus in EKS Anywhere package spec
Example
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: generated-prometheus
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: prometheus
targetNamespace: observability
config: |
server:
replicaCount: 2
statefulSet:
enabled: true
Configurable parameters and default values under spec.config
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| rbac.create |
Specifies if clusterRole / role and clusterRoleBinding / roleBinding will be created for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
true |
| sourceRegistry |
Specifies image source registry for prometheus-server and node-exporter |
"783794618700.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com" |
| Node-Exporter |
|
|
| nodeExporter.enabled |
Indicates if node-exporter is enabled |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostNetwork |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host network namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.hostPID |
Indicates if node-exporter shares the host process ID namespace |
true |
| nodeExporter.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies node-exporter image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| nodeExporter.image.repository |
Specifies node-exporter image repository |
"prometheus/node-exporter" |
| nodeExporter.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the node-exporter container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| nodeExporter.service |
Specifies how to expose node-exporter as a network service |
See footnote |
| nodeExporter.tolerations |
Specifies node tolerations for node-exporter scheduling to nodes with taints. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation toleration
field for more details. |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.annotations |
Specifies node-exporter service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.create |
Indicates if node-exporter service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.nodeExporter.name |
Specifies node-exporter service account name |
"" |
| Prometheus-Server |
|
|
| server.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is enabled |
true |
| server.global.evaluation_interval |
Specifies how frequently the prometheus-server rules are evaluated |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_interval |
Specifies how frequently prometheus-server will scrape targets |
"1m" |
| server.global.scrape_timeout |
Specifies how long until a prometheus-server scrape request times out |
"10s" |
| server.image.pullPolicy |
Specifies prometheus-server image pull policy: IfNotPresent, Always, Never |
"IfNotPresent" |
| server.image.repository |
Specifies prometheus-server image repository |
"prometheus/prometheus" |
| server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server container name |
"server" |
| server.persistentVolume.accessModes |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume access modes |
"ReadWriteOnce" |
| server.persistentVolume.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server will create/use a Persistent Volume Claim |
true |
| server.persistentVolume.existingClaim |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume existing claim name. It requires server.persistentVolume.enabled: true. If defined, PVC must be created manually before volume will be bound |
"" |
| server.persistentVolume.size |
Specifies prometheus-server data Persistent Volume size |
"8Gi" |
| server.remoteRead |
Specifies prometheus-server remote read configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_read
for more details |
[] |
| server.remoteWrite |
Specifies prometheus-server remote write configs. Refer to Prometheus docs remote_write
for more details |
[] |
| server.replicaCount |
Specifies the replicaCount for prometheus-server deployment / statefulSet. Note: server.statefulSet.enabled should be set to true if server.replicaCount is greater than 1 |
1 |
| server.resources |
Specifies resource requests and limits of the prometheus-server container. Refer to the Kubernetes API documentation ResourceRequirements
field for more details |
{} |
| server.retention |
Specifies prometheus-server data retention period |
"15d" |
| server.service |
Specifies how to expose prometheus-server as a network service |
See footnote |
| server.statefulSet.enabled |
Indicates if prometheus-server is deployed as a statefulSet. If set to false, prometheus-server will be deployed as a deployment |
false |
| serverFiles.“prometheus.yml”.scrape_configs |
Specifies a set of targets and parameters for prometheus-server describing how to scrape them. Refer to Prometheus docs scrape_config
for more details |
See footnote |
| serviceAccounts.server.annotations |
Specifies prometheus-server service account annotations |
{} |
| serviceAccounts.server.create |
Indicates if prometheus-server service account will be created |
true |
| serviceAccounts.server.name |
Specifies prometheus-server service account name |
"" |
18 - Metrics Server Configuration
Metrics Server is a scalable, efficient source of container resource metrics for Kubernetes built-in autoscaling pipelines.
Configuration options for Metrics Server
18.1 - Metrics Server
Install/upgrade/uninstall Metrics Server
If you have not already done so, make sure your cluster meets the package prerequisites.
Be sure to refer to the troubleshooting guide
in the event of a problem.
Important
- Starting at
eksctl anywhere version v0.12.0, packages on workload clusters are remotely managed by the management cluster.
- While following this guide to install packages on a workload cluster, please make sure the
kubeconfig is pointing to the management cluster that was used to create the workload cluster. The only exception is the kubectl create namespace command below, which should be run with kubeconfig pointing to the workload cluster.
Install
-
Generate the package configuration
eksctl anywhere generate package metrics-server --cluster <cluster-name> > metrics-server.yaml
-
Add the desired configuration to metrics-server.yaml
Please see complete configuration options
for all configuration options and their default values.
Example package file configuring a cluster autoscaler package to run on a management cluster.
apiVersion: packages.eks.amazonaws.com/v1alpha1
kind: Package
metadata:
name: metrics-server
namespace: eksa-packages-<cluster-name>
spec:
packageName: metrics-server
targetNamespace: <namespace-to-install-component>
config: |-
args:
- "--kubelet-insecure-tls"
-
Install Metrics Server
eksctl anywhere create packages -f metrics-server.yaml
-
Validate the installation
eksctl anywhere get packages --cluster <cluster-name>
Example command output
NAME PACKAGE AGE STATE CURRENTVERSION TARGETVERSION DETAIL
metrics-server metrics-server 8h installed 0.6.1-eks-1-23-6-b4c2524fabb3dd4c5f9b9070a418d740d3e1a8a2 0.6.1-eks-1-23-6-b4c2524fabb3dd4c5f9b9070a418d740d3e1a8a2 (latest)
Update
To update package configuration, update metrics-server.yaml file, and run the following command:
eksctl anywhere apply package -f metrics-server.yaml
Upgrade
Metrics Server will automatically be upgraded when a new bundle is activated.
Uninstall
To uninstall Metrics Server, simply delete the package
eksctl anywhere delete package --cluster <cluster-name> metrics-server
18.2 - v3.12.1
Configuring Metrics Server in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| args |
Additional args to provide to metrics-server
Example:
cloudProvider: ["–kubelet-insecure-tls"] |
[] |
18.3 - v3.8.2
Configuring Metrics Server in EKS Anywhere package spec
| Parameter |
Description |
Default |
| General |
|
|
| args |
Additional args to provide to metrics-server
Example:
cloudProvider: ["–kubelet-insecure-tls"] |
[] |
19 -
| AWS Region |
| us-east-2 |
| us-east-1 |
| us-west-1 |
| us-west-2 |
| ap-northeast-3 |
| ap-northeast-2 |
| ap-southeast-1 |
| ap-southeast-2 |
| ap-northeast-1 |
| ca-central-1 |
| eu-central-1 |
| eu-west-1 |
| eu-west-2 |
| eu-west-3 |
| eu-north-1 |
| sa-east-1 |




























